What other name is Vitamin B2 known by?
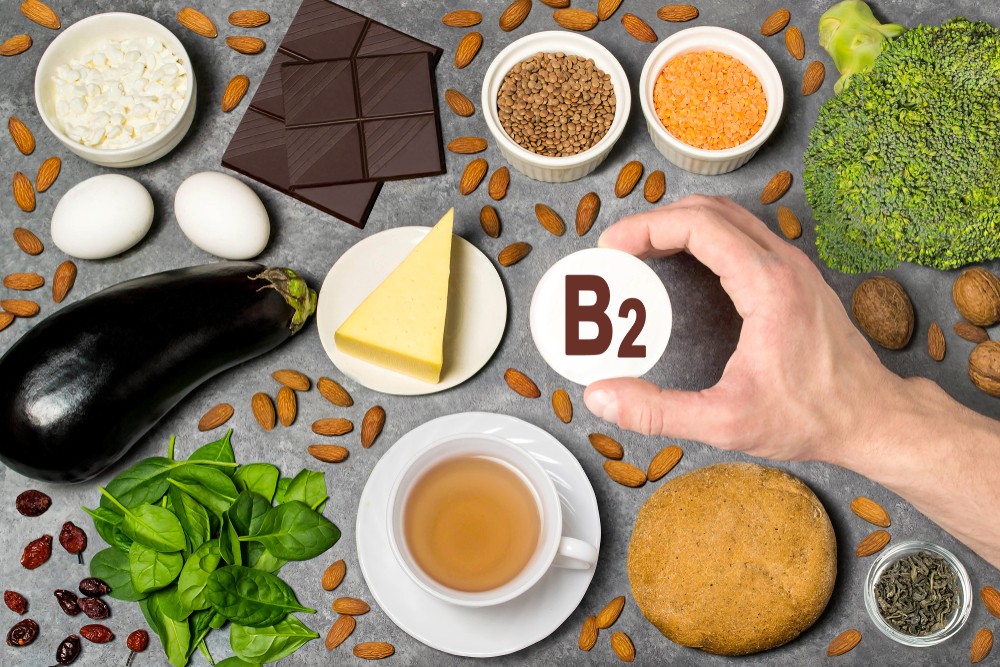

Riboflavin
Riboflavin is one of the B vitamins that are water-soluble.
A vitamin that you need in life! Take our quiz on what you know about vitamin B2!


Riboflavin
Riboflavin is one of the B vitamins that are water-soluble.

Ariboflavinosis
Ariboflavinosis is caused by a deficiency of Vitamin B2 (riboflavin). Certain groups of people are at a greater risk of being deficient in riboflavin.
It helps transport oxygen in the blood
Vitamin B2 is involved in red blood cell production and the transportation of oxygen to the cells. Improving the amount of riboflavin in the body can increase circulating haemoglobin levels and increase red cell production.

It helps convert carbohydrates into energy
Vitamin B2 is one of the 8 B vitamins. All B vitamins help the body to convert food (carbohydrates) into fuel (glucose), which is used to produce energy. These B vitamins, often referred to as B-complex vitamins, also help the body metabolise fats and protein.
It helps maintain healthy nerve cells
Vitamin B2 helps maintain healthy nerve cells and the nervous system function properly.

It protects against osteoporosis
When researchers looked at the role of vitamin B in bone health, they found that several different types of vitamin B appeared to help keep bones strong and protect against osteoporosis. The forms of vitamin B likely at work in this way were B2, B6, folate, and B12.
It boosts the immune system
Vitamin B2 is a heat-stable, water-soluble vitamin that the body uses to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and protein into glucose for energy. In addition to boosting energy, this vitamin functions as an antioxidant for the proper functioning of the immune system, healthy skin, and hair.

It reduces homocysteine levels
Vitamin B2 supplements taken daily can reduce homocysteine (a common amino acid in your blood. High levels of it are linked to the early development of heart disease) levels by up to 40% in some people. According to one study, a 25% reduction in homocysteine reduces the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) by 11% to 16% and the risk of stroke by 19% to 24%.

11 12

