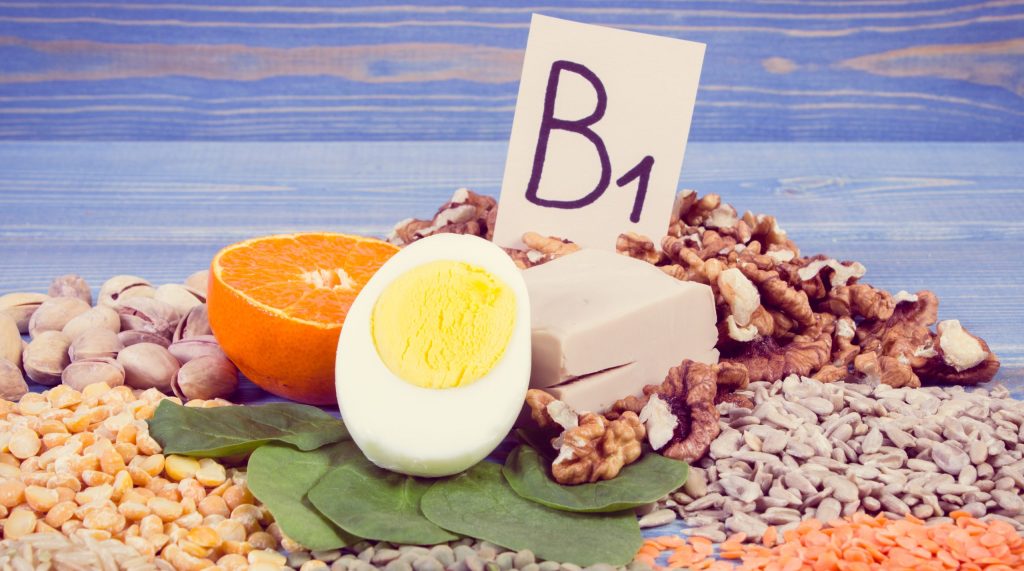
Thiamine, you have probably seen this term before, also known as vitamin B1, is often called the ‘peace of mind’ vitamin. All body tissues need this nutrient. Vitamin B1 takes care of all aspects of our health! It is essential for our bodies and its deficiency creates discomfort symptoms in us.
These days, more and more doctors are missing all of the nutritional information about vitamin deficiencies. Instead of helping people to deal with the problem, they prescribe huge lists of medicines with many side effects, when they could just solve the problem of vitamin deficiencies. Have you experienced this? Then join us!
Key functions – good stuff

Vitamin B1, or thiamine, is a water-soluble vitamin, as all vitamins of the B complex are. Vitamin B1 allows the body to use carbohydrates as energy. It is essential for glucose metabolism and plays a key role in nerve, muscle and heart function.
1Minimises the risk of heart disease
Vitamin B1 plays a key role in the production of acetylcholine. This is the element that helps your body transmit messages between your nerves and muscles. Without this communication, your heart will not work as it should. A lack of vitamin B1 is one of the causes of irregular heart function.
2Helps with kidney disease of people who have type 2 diabetes
One of the studies in patients with type 2 diabetes with kidney disease (microalbuminuria) showed a significant improvement after therapy with thiamine (vitamin B1). The first group of people received a dose of thiamine, while the second group received a placebo.
What is microalbuminuria? It is a pathology in which the kidneys excrete albumin protein (it is synthesized by the liver and found in the blood. It is the most abundant protein in human plasma, making up about 60% of the total protein content) in amounts greater than normal.
After the treatment period, patients receiving thiamine therapy had decreased (17,7 mg) urinary albumin excretion compared to patients who received a placebo (35,5 mg) within 3 months.
3Protects the brain
Vitamin B1 helps to bridge the gap between the connection of the brain and the body. It can help protect from a cerebellar syndrome, a form of brain damage. Vitamin B1 helps develop the myelin sheath that covers the nerves, protecting them from damage and death. This vitamin is also known to improve concentration and memory. Because of its properties in improving memory and its ability to positively influence the health of the nervous system, this vitamin is commonly referred to as the ‘moral vitamin.’
The study showed that 13.3% of elderly patients with cognitive impairment who developed an acute onset of behavioural disorders had vitamin B1 deficiency. It can therefore be concluded that vitamin B1 deficiency is a potential contributing factor exacerbating the symptoms and signs of cognitive impairment in elderly patients, says the study.
4Ensures healthy metabolism
Vitamin B1 is needed by the body to create ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), the main energy molecule in the body. It helps in the conversion of carbohydrates into glucose, which is the main source of energy the body needs to maintain normal metabolism. It also helps to break down proteins and fats.
5Provides your body with energy
Vitamin B1 plays an important role in converting energy for the body from nutrients. Like other B-complex vitamins, it is sometimes called an ‘anti-stress’ vitamin because it can strengthen the immune system and improve the body’s ability to cope with stressful conditions. Vitamin B1 is found in food of plant and animal origin and plays a crucial role in some metabolic reactions. Your body needs it to make ATP, which every cell in the body uses to make energy.
Specific features
Vitamin B1 dissolves in water and is not deposited in the body. Because of this, they need to be replenished regularly through the diet.
Bad news if there is a deficiency

Vitamin B1 deficiency usually leads to beriberi, a disease that affects breathing, eye movement, heart function and alertness. This is caused by a build-up of pyruvic acid in the blood, which is a side effect of your body not being able to turn food into fuel. Also, another symptom of vitamin B1 deficiency is weight loss and anorexia.
Mental problems may occur, including confusion and short-term memory loss. Muscles may become weak and cardiovascular symptoms such as an enlarged heart may occur. Fortunately, vitamin B1 deficiency is rare in developed countries and not frequent in healthy adults. It is more common in people with certain medical conditions. Conditions that can also reduce vitamin B1 levels include alcoholism and Crohn’s disease.
Interesting Fact from Healthypedia
Although symptoms of vitamin B1 deficiency were first recorded in ancient texts of Chinese medicine, they were not associated with the diet until the late 19th century. In 1884, a Japanese physician noted a very high rate of morbidity and mortality among Japanese sailors who ate only rice for several months at sea. When they began to eat a more varied diet, including whole grains, meat, beans and vegetables, the rate of disease and death almost disappeared. Around the same time, two Dutch scientists observed that chickens fed white polished rice developed leg paralysis, whereas chickens fed brown unpolished rice did not. Their observations led to the discovery of thiamine (vitamin B1) present in the outer layers of rice, which had been removed during polishing.
Bad news if over-consumed or overloaded
An overdose of vitamin B can lead to symptoms ranging from mild to severe.
Skin rash
One common side effect of an overdose of vitamin B is a skin rash. There may be complaints of an itching sensation all over the body. The extent of the skin rash depends on the intensity of the B vitamin complex overdose.
Gastrointestinal problems
Another common side effect of vitamin B overdose is gastrointestinal problems. When a higher dose of vitamin B is taken, people may suffer from upset stomach, nausea or mild diarrhoea. People with a history of gastrointestinal problems and the elderly are more likely to suffer from severe stomach cramps and severe diarrhoea after taking high doses of vitamin B.
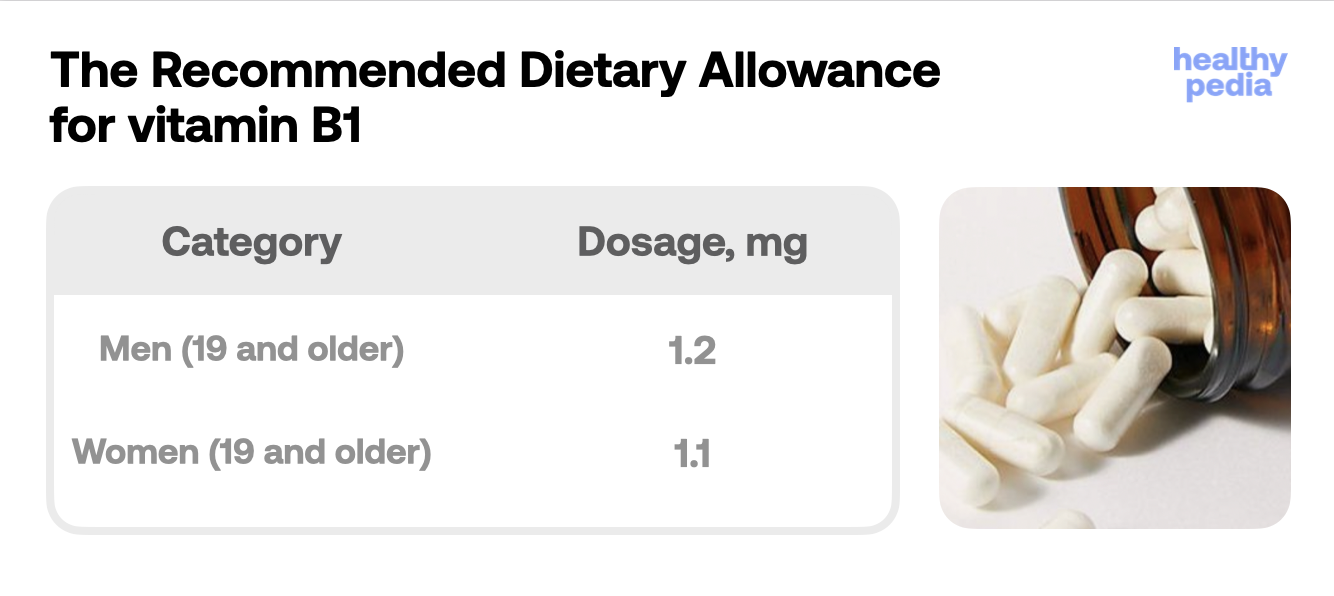
How much vitamin B1 do we need? Norms and recommendations

The body cannot produce vitamin B1 on its own, so it must be obtained through the diet or in some cases through supplementation. The dose depends on why you need this vitamin and whether it has been prescribed by your doctor.
If your child is prescribed vitamin B1, your doctor will base the dose on your child’s weight to determine the correct dose.
Best ways to get vitamin B1

Vitamin B1 is found in meat, fish and whole grains. It is also added to bread, cereal and baby formula. These are excellent sources of this vitamin.
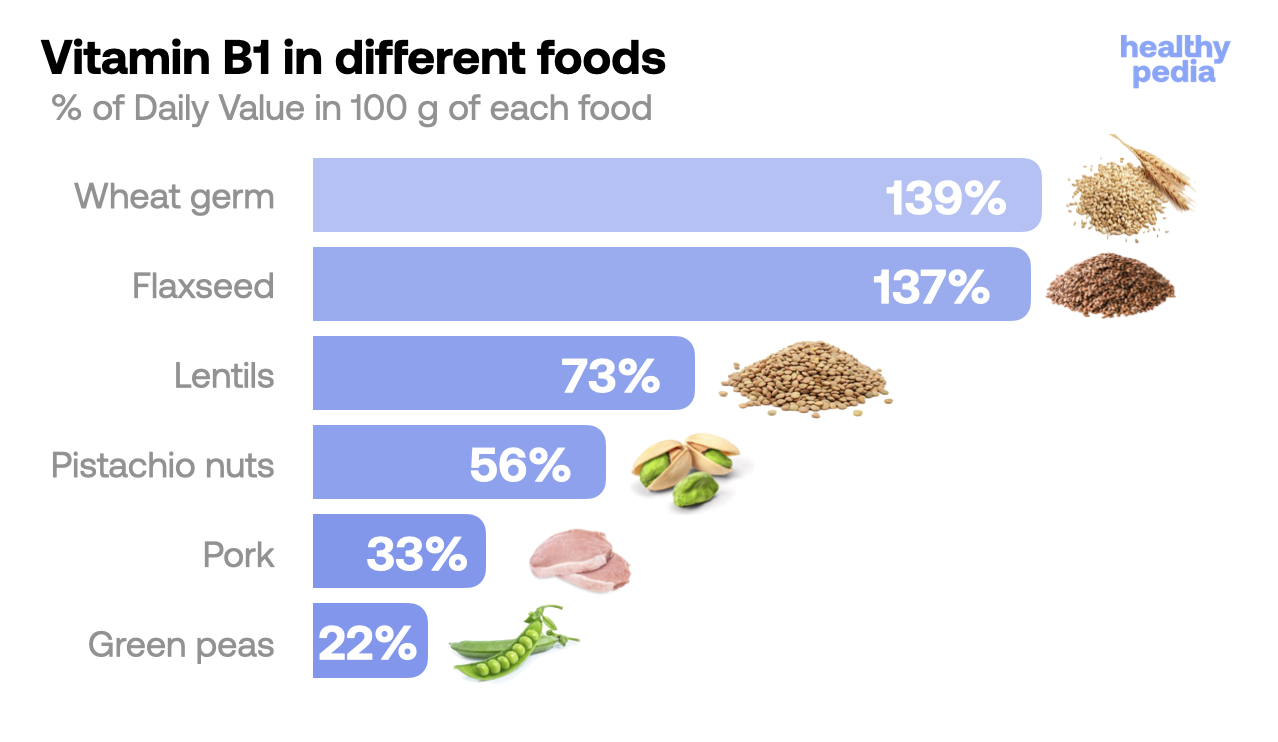 Source: USDA
Source: USDA Most cost-efficient ways
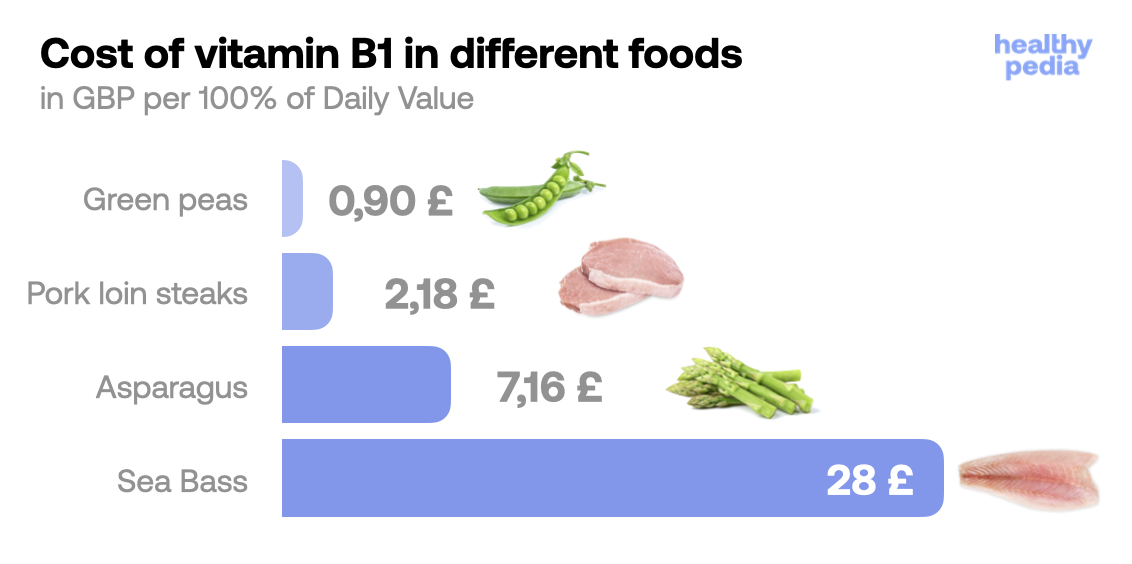 Source: Healthypedia
Source: Healthypedia Supplementation
Vitamin B1 intake should be through a balanced diet. You should avoid taking vitamin B1 supplements as there is a wide range of foods rich in vitamin B1 and these are much healthier and tastier than the chemical component in the capsule.
Also taking supplements carries the risk of incompatibility with medicines or even side effects in some people due to overdose. You should therefore consult a healthcare professional before taking vitamin B1 supplements.
What reduces the effect of vitamin B1?

Vitamin B1 is destroyed by high heat or prolonged cooking. It is also leached into the water and is lost in any boiling or soaking water that is discarded. It can also be removed by processing foods such as refined white bread and rice, which is why vitamin B1 is fortified or added back into many processed baked goods, cereals, and grains.
Did you know?
-
Vitamin B1 is the only vitamin in the B vitamin group found more in plant foods than in animal foods.
Let’s sum up

Vitamin B1 is essential for human health. All body tissues need this nutrient. You can get enough of this vitamin from a different food, animal-based and plant-based. This vitamin will provide your body with energy, protect your heart and brain and keep your metabolism in good condition.
Not enough? Here is more
In this video, by Dr. Berg, you will find out more about the symptoms you may have if you have a vitamin B1 deficiency. Dr Berg specializes in healthy ketosis and intermittent fasting. He is the director of Dr Berg’s Nutritionals and a best-selling amazon.com author.