Vitamin B3, also known as niacin, was first discovered in the early 20th century. At the time, a disease called pellagra was causing mass suffering and death in the southern United States. Pellagra was characterized by symptoms such as skin rashes, diarrhoea and confusion, and was generally common among people who lived in poverty and ate a low-nutrient diet.
In the early 1900s, Dr. Joseph Goldberger, a public health specialist, was commissioned to discover the cause of pellagra and find a cure. He and his team conducted a series of experiments, feeding different groups of people various diets to see if they could replicate the symptoms of pellagra. In the end, they discovered that pellagra was caused by a deficiency in a nutrient they called the ‘PP factor’, which we know today as vitamin B3.
Dr. Goldberger’s discovery of vitamin B3 was a significant breakthrough in nutrition and helped save countless lives. Today, vitamin B3 is an important nutrient known to have many health benefits.
Key functions – good stuff

When it comes to vitamin B3 health benefits, there are many different aspects to consider. Vitamin B3 is an essential nutrient that plays a key role in the body’s normal processes, ranging from energy production and heart health to brain function and skin health. As such, getting enough vitamin B3 each day can help support overall well-being and reduce the risk of various chronic diseases.
1Supports cardiovascular health
Vitamin B3 has a positive effect on cardiovascular health. It can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke, and improve blood flow. Vitamin B3 can support cardiovascular health in several different ways. For example, it can help reduce bad cholesterol synthesis in the liver, which can lower blood cholesterol levels.
Vitamin B3 may also have anti-inflammatory effects, which may help to reduce the risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
2May help to improve insulin sensitivity in the body
Insulin sensitivity means how well the body’s cells respond to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When cells are more sensitive to insulin, they absorb glucose from the bloodstream better, which helps to keep blood sugar levels in a healthy range.
Vitamin B3 can improve insulin sensitivity in several different ways. For example, it can help to increase the number of insulin receptors on the surface of cells, which increases the ability of cells to respond to insulin. Vitamin B3 can also influence the production of certain enzymes and hormones that are involved in regulating blood sugar levels.
Vitamin B3 plays an important role in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and can be useful for people with or at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
3Improves brain health
Vitamin B3 is involved in the production of neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit signals in the brain and nervous system. It is also part of NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a molecule that plays a key role in energy metabolism in the brain.

Preliminary research suggests that Vitamin B3 may also help keep the brain healthy in the case of Alzheimer’s disease. However, the results are mixed. For example, the study says that elevated plasma homocysteine levels are a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. This global study that involved a group of about 20,000 people showed that homocysteine levels were reduced by 28% in cognitive areas, but had no effect on global cognitive function or on cognitive ageing.
4Enhances nervous system function
Vitamin B3 plays a crucial role in the functioning of the nervous system. It helps to maintain the normal function of the brain and nervous system and may help to reduce the risk of certain neurological disorders.
5Helps convert food into energy
Vitamin B3 plays an important role in the metabolism of food and the production of energy. It is involved in the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and helps to convert these nutrients into energy that the body can use. Vitamin B3 is part of a molecule called NAD (we mentioned above), which helps the body use nutrients from food to make energy.
6Maintains healthy skin, hair, and mucous membranes
Vitamin B3 helps to keep the skin healthy by maintaining the integrity of the skin barrier and reducing inflammation. It may also help to prevent acne and improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin. Vitamin B3 can also help ward off certain skin cancers. After 12 months in a study of a group of more than 300 people after taking niacin, the incidence of new non-melanoma skin cancers was 23% lower.
Vitamin B3 is also important for the health of hair and mucous membranes, such as those found in the mouth and nose.
 Source: National Library of Medicine
Source: National Library of Medicine Specific features
Vitamin B3 is water-soluble, which means that it dissolves in water and is not deposited in the body.
Like all B vitamins, vitamin B3 helps convert food into energy by assisting enzymes. In particular, this vitamin is a major component of NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), two coenzymes involved in cellular metabolism. It also plays a role in cell signaling, DNA creation and repair, and acts as an antioxidant.
Bad news if there is a deficiency

Vitamin B3 deficiency is rare in industrialised countries as it is well-absorbed from most foods and is added to many products and multivitamins. Severe niacin deficiency leads to pellagra, a disease that causes a dark, sometimes scaly rash on skin areas exposed to sunlight; a bright reddened tongue; and constipation/diarrhoea.
Other signs of severe vitamin B3 deficiency include:
-
Depression
-
Headache
-
Fatigue
-
Memory loss
-
Hallucinations
Bad news if over-consumed or overloaded
Although vitamin B3 is an essential nutrient and important for general health, too much of it can be consumed. You are unlikely to overload your body with this vitamin with food. But supplements carry a very real risk. High doses of vitamin B3 supplements can have side effects, such as:
Hyperaemia: Vitamin B3 can cause blood vessels in the skin to dilate, which can cause a feeling of heat and reddening of the skin.
Dizziness: Large doses of vitamin B3 can cause dizziness or lightheadedness.
Nausea: Some people may experience nausea or upset stomach when taking high doses of vitamin B3.
Damage to the liver: In rare cases, high doses of vitamin B3 can cause liver damage.
How much vitamin B3 do we need? Norms and recommendations

The Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academy of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine in the USA has developed guidelines for the human daily intake of vitamin B3.
Here are the recommendations.
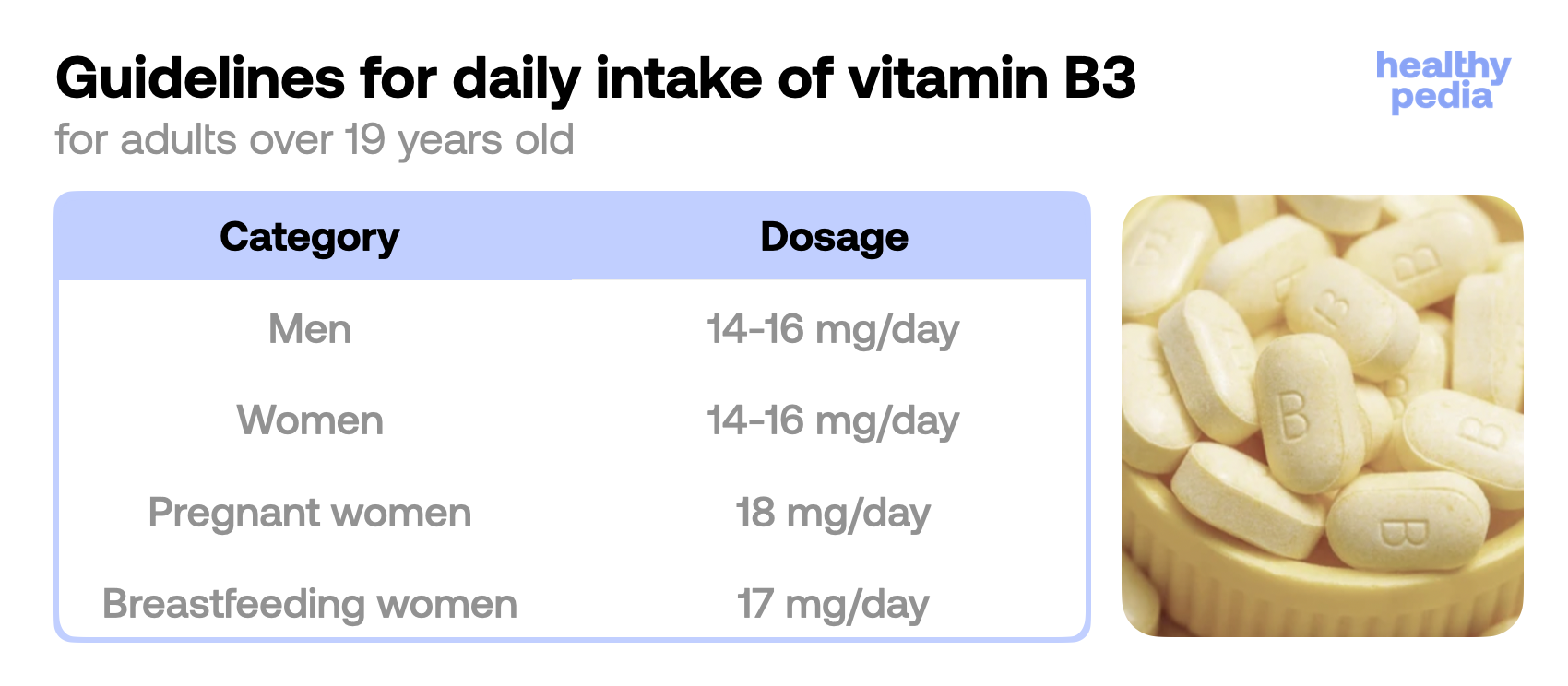 Source: National Academies
Source: National Academies Best ways to get Vitamin B3

So if you want to increase your own intake of vitamin B3 you have plenty of options to choose from. Excellent sources of vitamin B3 include meat, fish, eggs, green leafy vegetables, beans and nuts. Vitamin B3-rich foods are the best way to maintain good levels of this vitamin in the body.
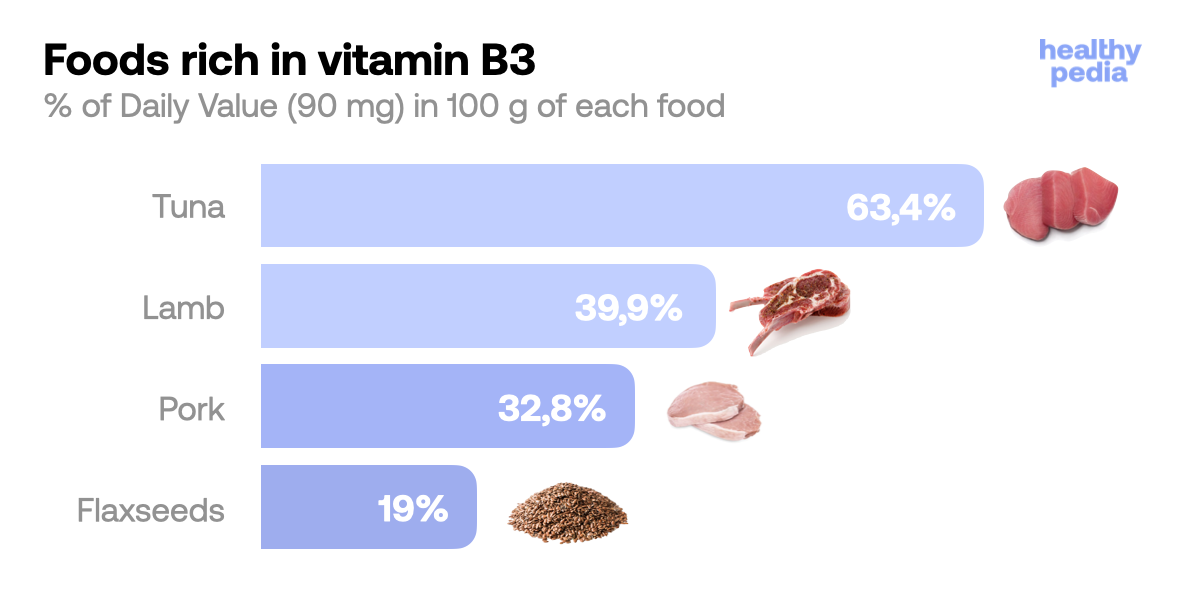 Source: USDA
Source: USDA Most cost-efficient ways
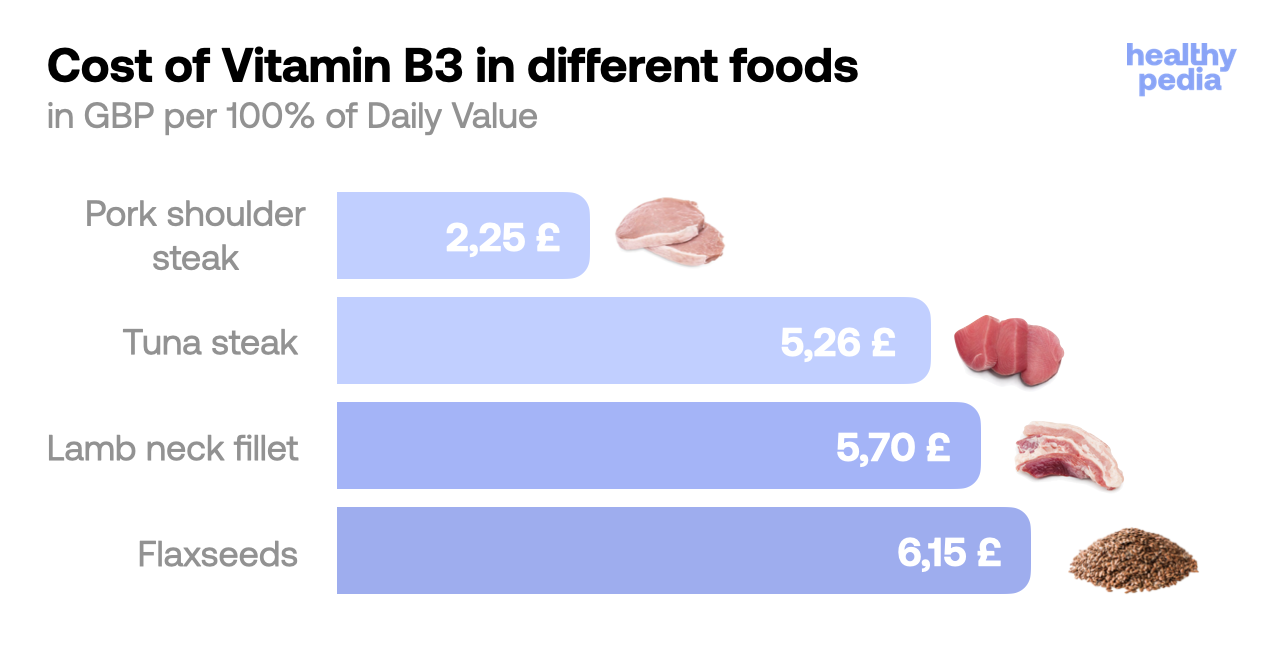 Source: Healthypedia
Source: Healthypedia Supplementation
When we neglect a balanced diet in favour of various supplements, we also should remember that the importance of a complete diet cannot be overstated and supplements are not a substitute for it. Plus, taking supplements without a doctor’s prescription carries the risk of incompatibility with medicines or even side effects in some people due to overdose. Therefore, if you decide to take a vitamin B3 supplement, you should consult a healthcare professional first.
What reduces the effect of vitamin B3

Vitamin B3 is a stable nutrient that does not easily break down. It is not sensitive to heat, light, or oxygen, which means that it does not easily degrade during cooking or storage.
However, vitamin B3 can be lost from food when it is overcooked or when it is soaked in water for a long period of time. For example, boiling vegetables or soaking them in water can cause some of the vitamin B3 to leach out into the cooking water.
Did you know?
-
Vitamin B3 was first isolated from the black pepper plant in 1867 by chemist Adolf von Baeyer. He named it niacin, which is derived from the Latin word niacinum, meaning niadic acid.
-
Vitamin B3 is also known as nicotinic acid or niacinamide. Nicotinic acid is the form that is most commonly used for medicinal purposes while niacinamide is the form that is most commonly found in food.
Let’s sum up

Vitamin B3 is an important nutrient that plays a crucial role in many body functions. It is involved in energy production, helps to improve insulin sensitivity, maintains healthy skin, and hair and supports brain health and the functioning of the nervous system. It also has a positive effect on cardiovascular health and is found in a variety of foods, including meat, fish, poultry, nuts and seeds.
Not enough? Here is more
A very interesting video from our favourite Dr. Berg on what you need to know about vitamin B3 and schizophrenia. Dr. Berg is a chiropractor who specializes in Healthy Ketosis & Intermittent Fasting. He is the author of the best-selling book ‘The Healthy Keto Plan’ and director of Dr. Berg Nutritionals.








