Throughout history, eggs have been a staple in our diet and originated in South East Asia around 7500 BC when chickens were domesticated.
Until the 16th century, eggs began to catch on as a nutritious and inexpensive breakfast dish. In 1620, the English medical writer Tobias Venner recommended eating poached eggs for breakfast, and in 1669 one of the oldest cookbooks suggested eating two eggs for breakfast.
After the Industrial Revolution, consumption and production of eggs increased as they became an important breakfast product, which made eggs very desirable, eggs and egg dishes became a symbol of wealth in the 19th century.
To this day, eating eggs for breakfast remains one of the most popular and nutritious food options.
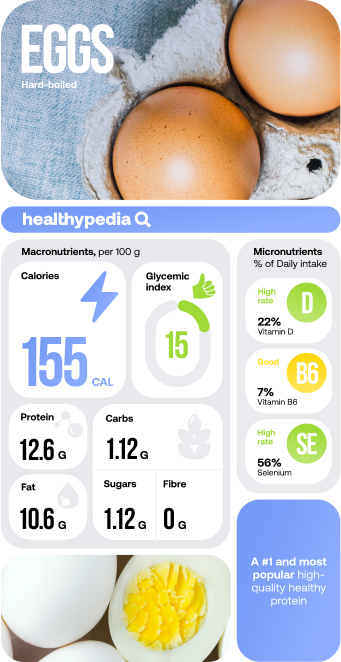
Eggs – Nutrition facts

Eggs have a medium energy value, and a good amount of protein and fat. In addition to this, there is a small number of carbs and sugar, no fibre and a low glycemic index which is good for blood glucose levels.

Eggs – Good news

Whole eggs are one of the most nutritious foods on the planet, they contain almost all the nutrients you need. The number of calories in an egg depends on its size. But a small egg can have slightly fewer calories than a large one.
1Serve as the best source of animal protein for your muscles
Protein in eggs is superior!
Protein is the basic building block of the human body. One large egg contains 6 grams of protein which makes it an excellent protein source. It has an anabolic effect which means that eggs have the ability to build protein tissues in your body and the percentage of how much egg protein is converted into body protein. Like your muscles, your joints and other proteins as well, so if we exclude the breast milk, the protein is at 48, meaning 48% is turning into body tissue. If we are talking about meat or fish, it’s only 32%, soy protein is 17%, and as a side note, egg white is only 17%. When you add the yolk you have even more use. Whey protein is only 16%. One part of this protein is converted into glucose and is used as fuel.
The next interesting point is the insulin index. It is the scale of how a non-carbohydrate food influences insulin and whole eggs with cholesterol have a much lower insulin effect than egg whites. So the more you take out the fat and have it as a pure protein, as in whey protein, the higher the insulin spike is.
So eggs are the best protein for you compared to anything else!
2Keep your liver and brain healthy
Eggs are considered to be one of the most nutritious foods on the planet.
Eggs are the main source of Choline, which is mainly concentrated in the yolk. It is believed that hard-boiled eggs are the second main source of Choline after beef liver (196% per 100 grams). Choline stimulates regeneration processes in liver tissue and is indicated in cases of liver damage caused by viruses, medication and alcohol. Choline acts as a bile salt in your liver, it helps to break down cholesterol so it’s a good antidote for gallstones and fatty liver disease, plus normalises liver function.
And then we get to lecithin which is also a good antidote that keeps your cholesterol levels in check.
Choline is good for your brain, it builds cell membranes and plays a role in the production of signalling molecules in the brain, among other functions.
Eggs also contain various micronutrients that are important for health. Eggs are an almost perfect food. They contain a little bit of almost all the nutrients you need for a healthy life.
Eat two eggs a day and they will cover from 10% up to 30% of your vitamin needs. Two eggs a day keep the doctor away!
3Can make you see through a brick wall
It’s a joke. Eggs can’t do it. But eating eggs definitely can improve your eyesight.
Eggs have carotenoids which are nutrient-dense pigments that give the yolk its colour, also they have a lot of health benefits.
Eggs contain two big carotenoids: lutein, which is yellow in colour, and zeaxanthin, which is more orange. Both of these pigments greatly improve eyesight. They support the lens and the retina and help prevent macular degeneration. They help to reduce the blue light you’re exposed to with all your gadgets.
One study examined egg consumption and uptake of lutein in people in their sixties. The results showed that eating 1 egg a day for 5 weeks, significantly increased serum lutein and zeaxanthin concentrations in the bodies of the elderly.
Another study observed that eating just 1.3 egg yolks a day for 4.5 weeks increased blood levels of lutein by 28-50% and zeaxanthin by 114-142%.
Given the positive link between lutein and zeaxanthin in terms of age-related eye disease, you should get more of these nutrients in your daily diet. Follow the recommendation to eat 2 eggs a day and add more green vegetables to your diet.
4Improve the strength of bones due to high Vitamin D and Vitamin K2
Eggs contain one of the highest amounts of vitamin D among all foods. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones and teeth, muscle function and the regulation of the immune system.
Vitamin D is needed for several reasons, including:
-
Bone development in children and skeletal health in adults
-
Absorption and metabolism of calcium and phosphorus
-
Regulation of the immune system
If your body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, you risk having weak bones. To avoid this, it is important to ensure you get enough vitamin D daily. An interesting fact about eggs is that they have a decent amount of Vitamin K2 which keeps calcium out of the arteries and keeps the calcium out of joints. So Vitamin D and Vitamin K2 work together.
According to the study, to maintain vitamin D levels throughout the year you need 10-15 mcg of vitamin D per day in your diet.
5Have a long-lasting filling effect
You might notice that eating eggs for breakfast may keep you feeling fuller for longer — this is usually due to the high protein content of eggs. Whether you have an omelette for breakfast or a hard-boiled egg as a snack, eggs can help you satisfy your hunger after or between meals.
Eggs also rank high on a scale called the satiety index. This scale evaluates how well foods help you feel full and reduce calorie intake later in the day.
6Help your child even before birth
There are different types of foods that are recommended for pregnant women. These foods are often rich in a lot of nutritional benefits. Pregnant women are urged to eat eggs because they contain folate. Folate is essential for the development of the fetus and makes eggs a great product to eat when you are expecting. Women that are looking for a healthy diet that will nourish their growing baby can take advantage of adding eggs to their nutrition.
7Boost your metabolism
Eggs contain a good balance of all of the essential amino acids that your body needs. This means your body can easily use the protein in eggs for maintenance and metabolism. Eating a high-protein diet has been shown to boost metabolism up to 80–100 calories a day through a process called the thermic effect of food. The thermic effect of food is the energy the body needs to metabolise food, and it is higher for protein than for fat or carbohydrates. This means that foods high in protein, such as eggs, can help you burn more calories to maintain weight loss.
8Fight depression and anxiety because of OMEGA-3 inside high-quality eggs
Omega-3-enriched eggs are produced when hens have a special diet that’s rich in ground flax seeds. Other premium ingredients like fish oil and minerals in hen’s feed, make eggs acquire much higher levels of nutrients like DHA, lutein and vitamin D3.
A diet that brims with Omega-3 eases intrusive thoughts, and depression and may be effective in stabilizing mood and increasing the effectiveness of conventional antidepressants. Omega-3s can easily travel through the brain cell membrane and interact with mood-related molecules inside the brain. They also have anti-inflammatory actions that may help relieve depression.
Omega-3 fats are famous for their health benefits, and rightfully so, and while most understand that fish and seafood are good sources, people are also pleased to know they have alternatives. Enriched with Omega-3 eggs play a role in helping people to get their daily dose of these superstar fats.
If you don’t eat fish regularly, but you do eat eggs, replacing your sources of Omega-3 with eggs, fortified with this vitamin, will allow you to increase your Omega-3 intake. You do not need to change any habits, or routines or alter the diet in a difficult way. Considering that the current recommended intake of Omega-3 fats for adults is between 250 and 500 mg per day, two with 180 mg EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)+DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) will help you to reach your goal.
9Do not make you gain weight
One large egg contains nearly 74 calories, yet it’s very high in nutrients. Egg yolks are especially nutritious.
An egg meal commonly consists of about 2–4 eggs. Three large boiled eggs contain less than 230 calories.
By adding a generous serving of vegetables, along with a source of fibre and fat like sliced avocado, you can have a meal of 500 calories. Additionally, consuming a diet high in protein may reduce the desire to eat by up to 15%. It may also help to prevent unhealthy late-night snacking.
10Do not cost a fortune and are easy to cook
Including eggs in your diet is very easy. They are inexpensive, widely available, and can be prepared within minutes.
Eggs are delicious in almost every way you make them, but they are most often boiled, scrambled, made into an omelette, or baked.
A breakfast omelette made with a couple of eggs and some vegetables is an excellent and quick weight-loss(not gain)-friendly breakfast.
Eggs and cholesterol: A scary fiction story with a happy ending

Many of us are afraid of cholesterol and have little understanding of what it actually is. There is ‘good’ and ‘bad’ cholesterol. Let’s find out what type of cholesterol eggs include.
A large study involving 30,000 people reveals that consuming 300 mg of cholesterol per day was associated with a 17% higher risk of cardiovascular disease and an 18% increased risk of all-cause death. Just 3-4 eggs per week will increase the risk of heart disease by 6%.
This study is now valued by scientists because of completely FALSE information
Here’s why…
-
The data was collected during a single visit.
-
It was based on a questionnaire.
-
They did not look at the long-term eating pattern.
-
The study was partially supported by the American Heart Association due to significant conflicts of interest.
So, 300 mg of additional cholesterol will increase your risk of cardiovascular disease by 17% and the risk of death by 18%.
Here is the question: over the past 12 months how often did you consume deli-style ham or light or low-fat or fat-free meats in your lunch? Rarely, or never, about 1/4 of the time? about 1/2 the time, almost always. But who’s going to remember all the things that they have eaten? The data was collected during one single visit. It didn’t look at patterns over some time, it was a one-shot deal.
Now, did you know that your body makes cholesterol? Did you realize that the body makes 3,000 mg per day? Not everybody knows it. That is equivalent to consuming 14 eggs every single day and according to that FALSE study, eating 300 mg is going to increase your risk of heart disease, so it’s not true.
In fact, there are a few studies that will change the way you think about cholesterol and egg consumption: proof and more proof links.
Eggs – Bad news

The good news is that all bad news is about low-quality eggs. If you choose the right eggs, you don’t need to read any further. But if not, you should read the following information to avoid problems.
Some producers have been known to add antibiotics and other additives to chicken feed to make them grow quickly. This, of course, affects the quality of the eggs we consume. The choice of the producer should therefore be made responsibly.
Our bodies cannot produce Omega-6, so we have to get them from our diets. There is a recommended rate of 5-10% of daily calories from Omega-6 fats or an average of 11 to 22 grams. But most of us get more than enough, which can promote inflammation and constrict blood vessels. Most of us get 14-25 times more omega-6 fatty acids than, for example, Omega-3. This does not mean that you should reduce your intake of Omega-6, but a better balance between Omega-6 and Omega-3 is the most beneficial for health.
There are some products, you have to be more careful with when it comes to preventing food poisoning. Eggs are a food that you have to be cooked cautiously. Raw and undercooked eggs can contain salmonella and some types of harmful bacteria. Consumption of contaminated eggs can cause food poisoning.
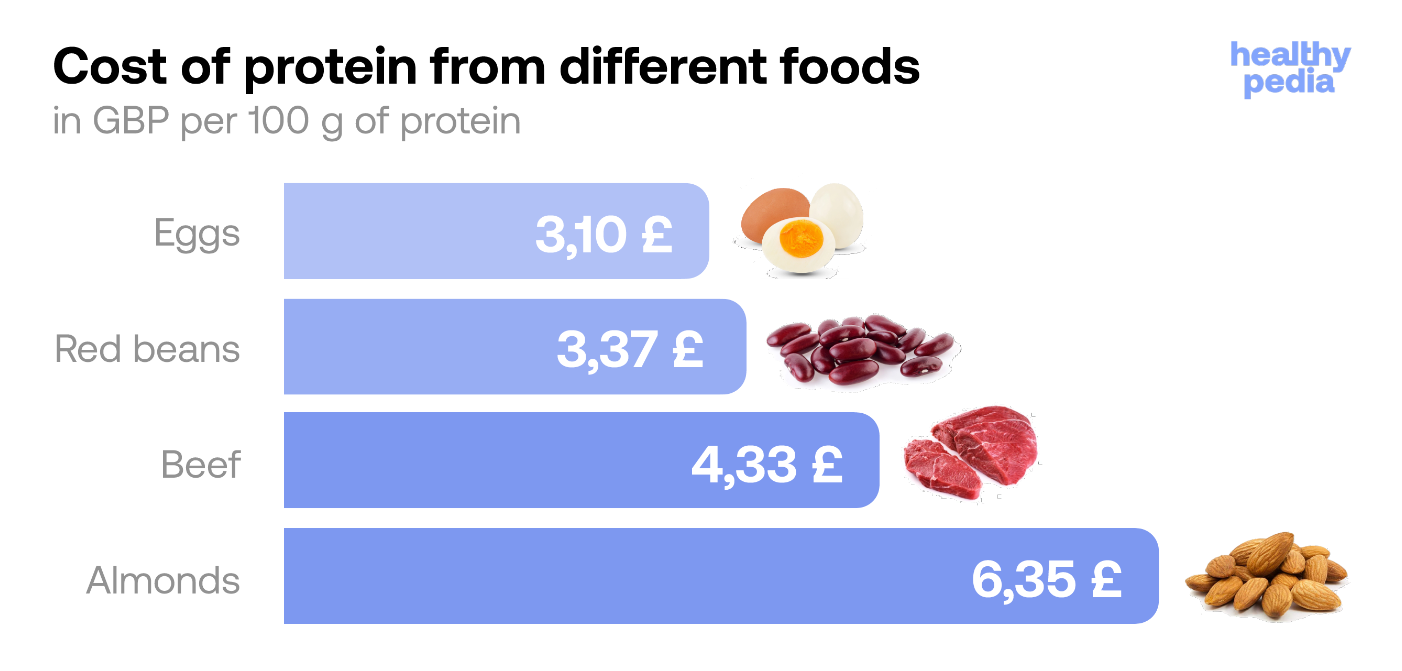
Cost efficiency in Great Britain
It seems like 100g of protein in eggs is one of the best options for getting protein on a budget. It is cheaper than, for example, more pricey protein in meat or nuts. The protein in eggs is a complete building block for your cells and muscles and the whole system.
 Source: Healthypedia
Source: Healthypedia Eggs in the Blue Zones
In the Blue Zones, people tend to eat only one egg two-three times a week. For example, Nicoya residents fry eggs and put them in corn tortillas, while on Okinawa Island they add a boiled egg to soup. Maybe, if they ate more eggs after reading this article, they would live even longer.
Fun & curious facts
-
How thick the eggshell will be, depends on the age of the laying hen
It is a common misconception that brown eggs have thicker shells than white eggs. The thickness of the shell depends solely on the age of the hen: young chickens lay eggs with a harder shell and older chickens lay eggs with a thinner shell. This thickness will occur regardless of the breed of hen or the colour of the eggs. -
Chickens’ earlobes can predict what colour of an egg they will lay
The colour of a chicken’s earlobes? Yes, chickens have earlobes that are a good indicator of the colour of the eggshells they will lay. As a rule, hens with white earlobes usually lay white eggs, and hens with red or brown earlobes lay brown eggs. The colour of the shell doesn’t affect the quality of the eggs so you don’t have to worry about this. -
All eggs start white
Despite the difference in colour at maturity, all eggs are white at the beginning of their development. -
Raw eggs are poorly absorbed by the body
Cooked eggs have a bioavailability of around 91% of protein, while protein from raw eggs only is 50% bioavailable (Evenepoel et al., 1998). This means that you can only absorb and utilize around 11 g of protein from your 180 g of raw eggs.
Eggs. Experiment by our expert
 Nutrition
Nutritionscore Blood glucose
trend
Just a couple of years ago, I discovered that eggs are the best protein source and healthy food in general. Though 15 years ago, eggs were thought to be villains because of the ‘cholesterol problem’ I still loved them. Science now confirms that eating eggs is not as dangerous as it was 20 years ago 🙂 and I love them even more 😇 The test result of my 4 medium eggs and blood glucose was as good as I expected. 9 out of 10. I will continue to love eating eggs and recommend doing it.
Let’s sum eggs up

Eggs are an excellent inexpensive source of many useful nutrients that can help you be healthy and fit at all times. You don’t have to worry about consuming eggs, they’re wholesome, you just have to make sure that they’re pasture-raised and organic. Eggs are nearly perfect, contain almost all the vitamins and minerals, and they are a great protein, healthy fat, low-carb product. You won’t regret including them in your diet as they also have the ability to fight bad moods and depression. Eat eggs and build up your felicity day by day – meal by meal.
Not enough? Here is more from our colleagues
In this video, our favourite Dr. Berg will tell you why you should eat eggs!










