If you are an owner of a smartwatch, we bet you have seen some sort of measurements concerning your activity levels. These could be; how many steps you’ve managed to make throughout the day, your current or resting heart rate, blood pressure, sleep quality and so on. Among all of those numbers, beats per second, hours and miles you could have come across the next abbreviation ‘VO₂ max’.
What exactly is it? Broken down, VO₂ max means the maximum (max) volume (V) of oxygen (O₂) your body can utilise during exercise. VO₂ max can give us a great deal of information about the capability of our bodies to perform daunting physical exercise, longevity and health overall.
What does VO₂ Max exactly mean?

VO₂ max measures the amount of oxygen and the speed at which it can be taken in through the lungs, transported through the bloodstream, and utilised by the muscles for energy production.
It is considered a key indicator of cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance. VO₂ max is measured in millilitres of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (mL/kg/min).
VO₂ Max on a cellular level

If you can remember back to school biology, you may remember the statement ‘mitochondria is a powerhouse of a cell.’ So, what exactly mitochondria is and how is it connected with VO₂ max?
Most energy in the body is produced by mitochondria, which are cellular organelles, meaning they have a particular job of producing energy by using oxygen (O₂). The amount of oxygen that the mitochondria can consume per minute determines VO₂ max.
The more mitochondria you have, the higher your VO₂ max and energy levels are. Thus, your VO₂ max is a good indicator of your mitochondrial health. In several studies, the mitochondrial content of the whole body has been found to be correlated with VO₂ max.
The decline in the number of mitochondria as we age may also explain an age-related drop in maximum oxygen uptake.
VO₂ Max defines cardiovascular fitness and endurance
VO₂ max can be determined by the efficiency of the body’s respiratory and cardiovascular systems, as well as the muscles’ ability to use oxygen to produce energy. The higher this level, the better the person’s cardiovascular fitness and endurance.
This can be proved, for instance, by cross-country skiers and their maximum oxygen volume levels. Cross-country skiing is an extremely challenging sport that requires great muscular and cardiovascular endurance. Cross-country skiers have been found to have extremely high VO₂ max levels of 70-80 mL/kg/min.
VO₂ Max as a health indicator
Besides being a direct indicator of fitness level, VO₂ max is also good in defining how healthy you are. As VO₂ max is dealing with the lungs and heart, it’s closely related to the disease risk of these two organs. It can also indicate a person’s overall metabolic health and risk for certain diseases such as COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) and certain types of cancer, as well as mental health.
Different studies suggest that improving your VO₂ by 3.5mL/kg/min can increase survival chances from chronic conditions by 10-25%.
 Source: AHA Journals
Source: AHA Journals How is VO₂ Max measured?

VO₂ max tests are typically performed in a laboratory and involve running on a treadmill and wearing a special mask. Even though this method is the most accurate, it is also the least accessible. Luckily, there are some ways to measure your VO₂ max manually.
The most obvious way is, for sure, to use a smartwatch. But if you do not have one you may calculate your VO₂ max by solving a couple of math equations. To do this use the resting and maximum heart rates method.
1. Count your resting heart rate (RHR): you may again use a smartwatch or place two fingers against the artery on the side of your neck and for 60 seconds count the beats you feel – that will be your resting heart rate.
Note: do this after a period of sitting for at least three minutes
2. Calculate your maximum heart rate (MHR): this can be calculated by multiplying your age by 0.7 and subtracting the result from 208: MHR = 208 – (Age x 0.7)
3. Define VO₂ max: the last thing you need to do is to divide MHR on RHR and multiply this result by 15.3.

There are also some other well-known methods to measure your VO₂ max that include walking and jogging. These are the Rockport walking fitness test and the Brigham Young University jog test.
What should your VO₂ Max be?

Now you know what VO₂ max is and how to measure it, you may come up with the questions of what is a ‘good’ VO₂ max and what level you need to be classed as healthy.
The thing is, the definition of ‘good’ VO₂ max is not universal for all people. Age, gender, fitness level, and the altitude you live at influence your maximum oxygen uptake. For instance, ladies tend to have lower VO₂ max levels than men due to genetics, men are naturally stronger and faster. Average inactive males and females achieve VO₂ max of around 35 and 40 mL/kg/min, respectively.
There is also a drop in VO₂ max levels related to the ageing process as cardiovascular function and muscle strength decline.
For a better understanding of how the classification moves across genders and ages, see the VO₂ max charts below.
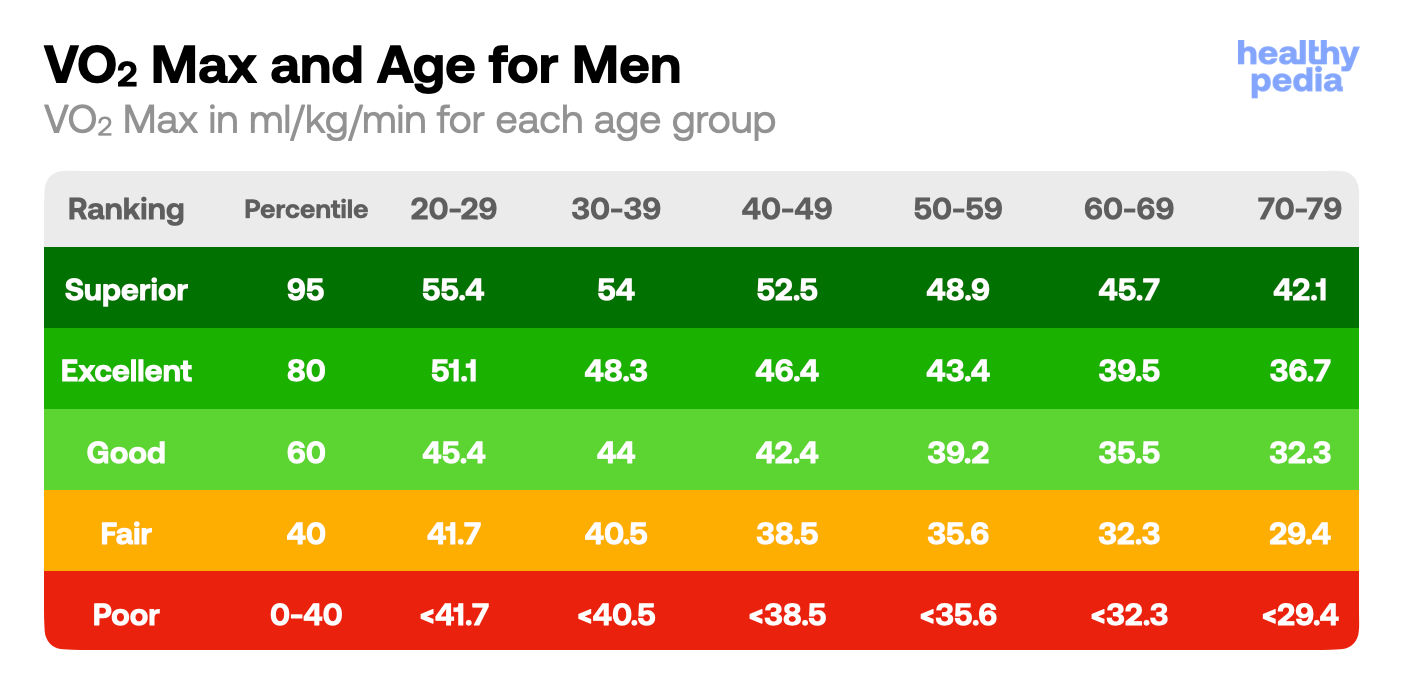
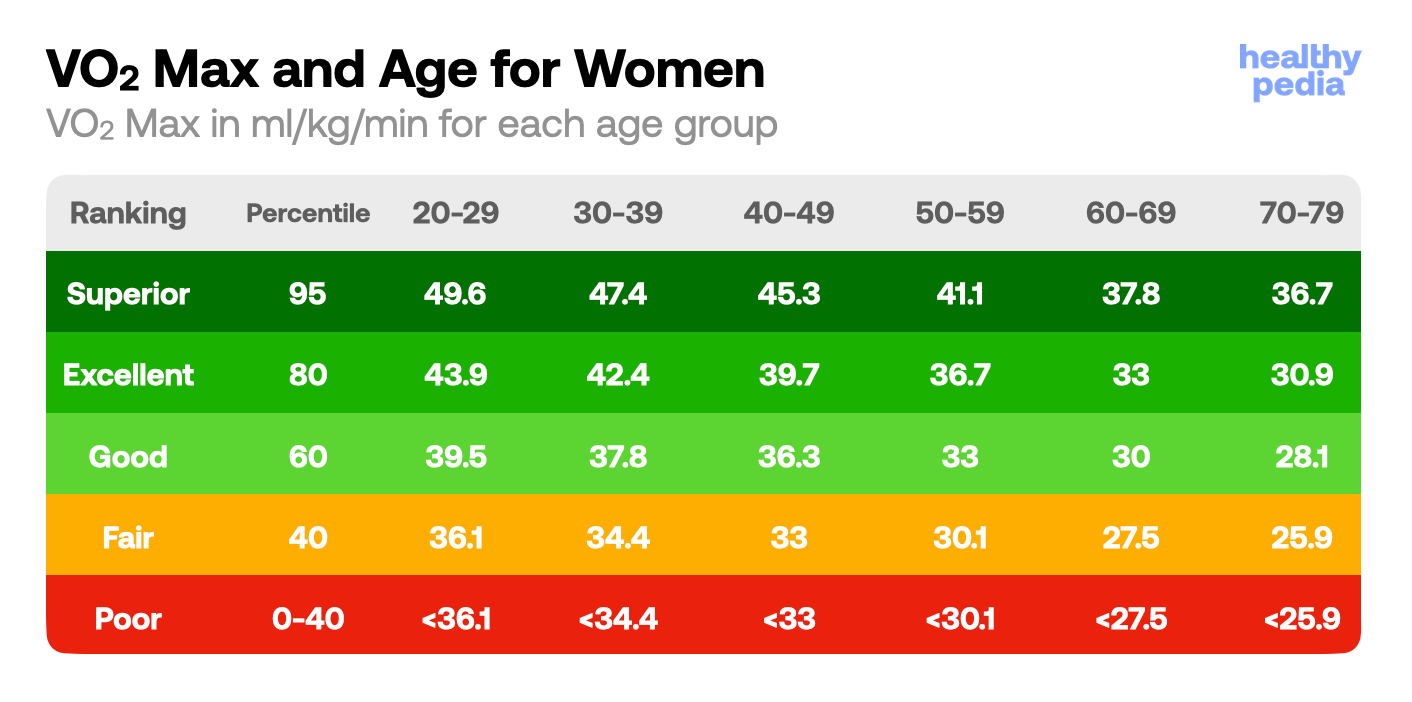 Source: The Cooper Institute
Source: The Cooper Institute If your VO₂ max is higher than the age group in which you are, then you are ‘younger’ than your peers. This is is also true in reverse.
Why should you increase your VO₂ Max?

The answer to this question appears to be pretty simple when considering the benefits of VO₂ max: a higher VO₂ max will help you live longer and be healthier.
No joke: Research published in Frontiers in Bioscience in 2018 found that increasing your VO₂ max can help maintain your health and fitness as you age.
As you improve your VO₂ max, you may notice other daily benefits, such as:
1Better endurance
The higher a person’s VO₂ max, the longer and harder they can perform physical exercise. If you improve your levels, you will be able to perform physical activity for longer periods of time without getting tired quickly.
2Improved cardiovascular function
Your heart and lungs will work more efficiently, delivering oxygen to your muscles quicker and more effectively. Improving your VO₂ max will also make you less likely to succumb to cardiovascular diseases. Just a 1 mL boost in maximum oxygen uptake reduces your risk of death from a heart attack by 3.2%.
3Stronger muscles

With improved cardiovascular function, your muscles will receive more oxygen, allowing them to work harder and become stronger.
One study shows that a maximum oxygen uptake raise of 5% after training, led to a higher quadriceps strength and outer thigh muscle strength increase by 100% and 28 %, respectively.
4Better metabolism
Your body will burn calories more efficiently, helping with weight loss and weight management. Even your resting metabolic rate will improve. This study says that people with higher VO₂ max levels also had better resting metabolic rates. This means that their bodies burned more calories even when t rest.
5Lower blood pressure
An improved cardiovascular function can lead to lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
 Source: Wiley Online Library
Source: Wiley Online Library Low maximum volume of oxygen level is related to a higher incidence of hypertension, while an improved VO₂ max would therefore be able to prevent or reduce the risk of hypertension. In a study of 3000 Japanese participants with 5 years of follow-up, people with poor fitness levels had a 10% higher chance of increased blood pressure when compared to a group with good VO₂ max levels.
6Reduced risk of chronic diseases
Improving VO₂ max and cardiovascular health can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
7Uplifted mood
Regular exercise is known for being a great dopamine booster. That’s why by improving your VO₂ max you are killing two birds with one stone, and this second bird is bad mood🙂 It has been shown that physical activity improves mood and reduces symptoms of anxiety and depression. In a study of nearly five thousand people, people who exercise regularly had a 25% lower chance of being diagnosed with major depression.
Let’s Sum Up

Knowing what VO₂ max is and being aware of your personal levels can be a powerful tool for measuring your overall fitness and wellness. It can help you identify areas for improvement and track your progress as you work towards a healthier and longer life. By understanding and actively working to increase your VO₂ max, you’ll be taking a significant step towards a fitter and more energised you.
Not enough? Here is more from our colleagues
The Peter Attia Drive is a weekly, ultra-profound podcast focusing on maximizing health and longevity. These videos are created by Peter who is a certified physician. He specialises in nutrition, exercise and sleep physiology, and emotional and mental health to enhance the quality of life and increase lifespan.
In this podcast, Peter breaks down what VO₂ max is, explains its history and explains why VO₂ max really matters.