VO₂ Max is an essential health indicator that is worth improving. Not only will it make you able to perform the physical exercise more often and for longer, but an increase in cardiorespiratory endurance will also make you live longer and healthier. The truth is very simple – the higher your VO₂ Max is, the better your health, longevity, and fitness.
But how do you know you should start improving it and how much should you improve it? For having this basis, you need, first of all, to measure your VO₂ Max and here is how.
Three methods to measure your VO₂ Max

VO₂ Max is your maximum oxygen consumption during intense physical activity. Since it calculates how efficiently your cells use oxygen for energy, this measurement is one of the best indicators of aerobic endurance and cardiovascular fitness.

It is possible to measure your maximum oxygen uptake in several ways, but most require equipment such as a treadmill or a special exercise cycle. It can be difficult to administer these tests, and they may not be appropriate for all fitness levels. Simple calculations or walking/jogging tests are the easiest ways to measure your VO₂ Max.
Method 1: through resting and maximum heart rates
Using resting and maximum heart rates for measuring your VO₂ Max may be the easiest way to calculate your maximum oxygen uptake. You just need to solve a few equations. Plus, this method is pretty convenient for personal trainers, when they meet their clients for the first time and need to know about a person’s cardiovascular fitness level. It can scare a new client out when on the first training session you ask them to perform a test running on the treadmill to their maximum exhaustion. Using this type of maximum rate of oxygen consumption measuring can come in handy as it doesn’t require any extra strenuous and daunting exercises.
1. Count Resting Heart Rate (RHR)
Many fitness watches or trackers come with the function of measuring your RHR so you may use this data. If you do not own such a device place two fingers against the artery on the side of your neck, just under your jaw. You should be able to feel your heartbeat on your fingers. For 60 seconds count the beats you feel – that will be your resting heart rate.
Note: Measure after sitting for at least three minutes.
2. Calculate Maximum Heart Rate (MHR)
The most common way of doing this is by subtracting your age from 220. But there are some controversies around this formula. So, for more accurate results multiply your age by 0.7 and subtract the result from 208.

For example, if Sarah is 35, her MHR will be:
MHR = 208 – (35 x 0.7) = 183.5
3. Define VO₂ Max with a simple formula
The last thing you need to do is to divide MHR on RHR and multiply this result by 15.3.

Method 2: Rockport walking fitness test
This method has two major advantages: the first is that it is easy to perform as all you need is a flat walking surface, and the second is that it can be performed by someone with pretty much any fitness level.
1. Warm up and measure your heart rate
Before you begin this test, try to walk slowly in circles, do some stretching and then measure your heart rate. You may either use a smartwatch or the 60-second method where you determine the number of beats per minute by counting your heartbeat over 60 seconds.
2. Walk 1 mile (1.6 km)
Now you have to start your stopwatch and walk the entire distance of 1 mile (1.6 km). Walk as quickly as possible but make sure you are not running.
3. Stop your stopwatch and measure your heart rate
When you are done with your walking, stop the stopwatch and jot down the time you needed to complete the task. After this, measure your heart rate once again. Continue to walk slowly for a while to cool down.
4. Calculate VO₂ Max
The Rockport VO₂ Max estimation depends on your gender, weight (in pounds), age, the time you needed to walk 1 mile, and your heart rate after you finished walking.
Then follow this formula:
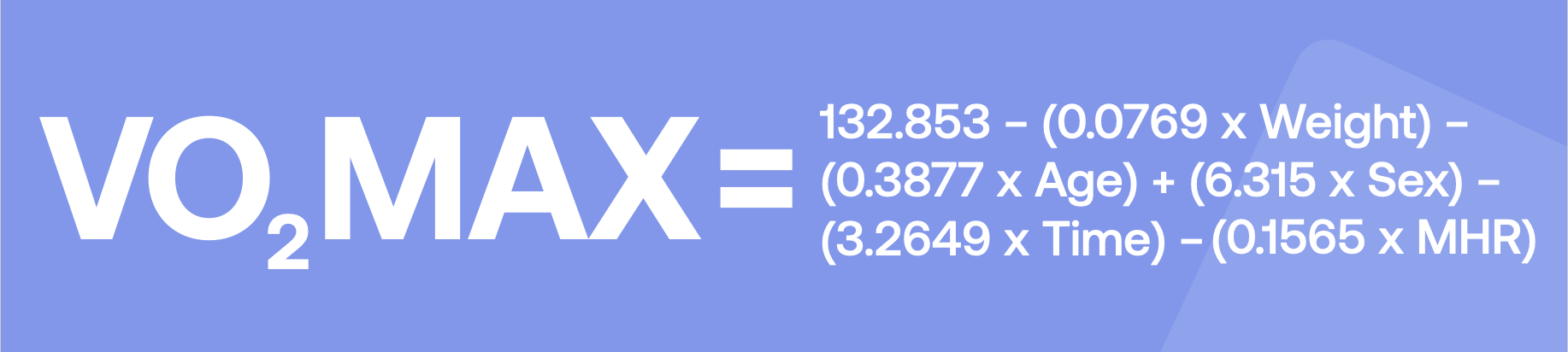
Note: the gender value for men is 1, and for women is 0.
Let’s take Sarah again as an example. She weighs 135 lb, is 35 years old, identifies as a female, needed 14 minutes to fulfil the walk and her heart rate after walking is 80.
VO₂ Max = 132.853 – (0.0769 x 135) – (0.3877 x 35) + (6.315 x 0) – (3.2649 x 14) – (0.1565 x 80)
Thus, Sarah’s VO₂ Max is 50mL/kg/min
Method 3: Brigham Young University jog test
Brigham Young University jog test is a simple and easy-to-use method, that defines your fitness levels via VO₂ Max. Even from its name, we see that it was invented to be used in physical education classes or in team practices. The test is most accurate for subjects aged 18-28, although younger people have been found to have an overestimated maximum oxygen uptake based on the results.
1. Start with warming-up
Before you begin an active part of this test don’t forget to warm up by walking slowly or stretching.

2. Start your stopwatch and lightly jog 1 mile (1.6 km)
Before you begin jogging, start the stopwatch. Then You should jog at a steady pace and not let your heart rate exceed 180 beats per minute. Jog no faster than 8 minutes per mile for men and 9 minutes per mile for women.
3. Track the heart rate
When you are done with your jogging, make sure to memorize or put down the timing. Plus, you should measure your heart rate either with a smartwatch or manually.
4. Do some calculations to get your VO₂ Max level
After you’ve completed everything above use the formula to receive the final results and get to know the level of your fitness.
Brigham Young University jog test has two equations that vary depending on your gender, so make sure to use the appropriate one not to get inaccurate results.


And back to Sarah: her weight is 61 kg, she needed 8 minutes to complete the jog and her heart rate was 140 bpm.
Thus, Sarah’s VO₂ Max = 100.5 – (0.1636 x 61 kg) – (1.438 x 8 min) – (0.1928 x 140 bpm) = 52mL/kg/min
Let’s sum up

Even though the most accurate results of your VO₂ Max levels can be obtained by using specialised equipment, you may get to know and monitor your level of fitness through the three methods discussed in this article. They’re easy to perform, do not require any special equipment, and can be completed by people of all fitness levels. Regardless of how you choose to measure your maximum rate of oxygen consumption, it is an important metric to keep track of to ensure that you are making progress in your fitness journey.
Not enough? Here is more from our colleagues
The Running Channel is a YouTube channel that aims to connect runners from all about the world through their videos. The channel provides interesting videos and podcasts on how to start, improve and make your runs more efficient.
Here, the hosts of the Running Channel have made a mini-investigation that compares VO₂ Max levels measured by a traditional lab estimation and a smartwatch one.