Are you ready to learn about one of the most important hormones in your body? We’re talking about insulin – the hormone responsible for regulating your blood sugar levels and keeping your metabolism and weight in check. You might have heard of insulin in the context of diabetes, but there’s so much more to this fascinating hormone than you might think.
In this article, we’re going to explore the ins and outs of insulin, from its role in protein synthesis and fat storage to how you can maintain healthy insulin levels. So grab a snack (but make sure it’s low in sugar!), sit back, and get ready to learn all about the hormone that keeps your body running smoothly.
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that has several crucial roles in the body. Primarily, it plays an important role in regulating weight and metabolism through its effects on glucose uptake and utilization, protein synthesis, and fat storage. Here is how insulin regulates weight and metabolism.
Insulin and glucose uptake and utilization
Glucose is a key source of energy for our cells and organs and is what powers all metabolic processes. Insulin promotes the uptake of glucose into cells and tissues, where it can be used for energy or stored as glycogen – the body’s source of fuel reserves.
For example, after a meal, your blood sugar (also known as blood glucose) levels spike, particularly if you eat something with a high sugar content like cake or chocolate. This rise in blood sugar is detected by the pancreas which releases insulin to act on target tissues such as the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue to promote glucose uptake and utilization. This removes glucose from the blood and restores blood sugar levels back to baseline.
The pancreas and insulin work together with another hormone called glucagon, which balances the actions of insulin, to maintain healthy blood glucose levels between a narrow range of 4-6mmol/L.
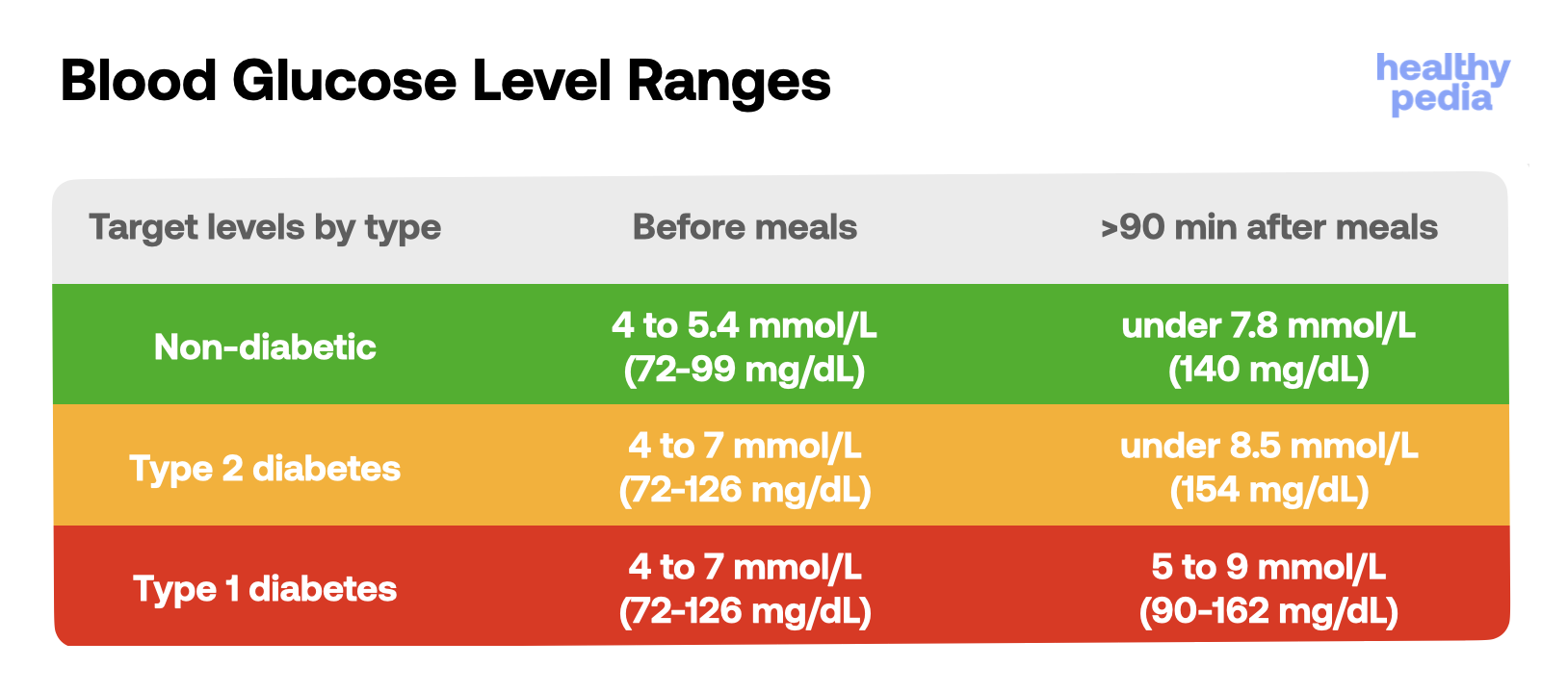 Source: diabetes.co.uk
Source: diabetes.co.uk Without insulin, glucose cannot enter cells and tissues, leading to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). This can cause a variety of symptoms and complications, including fatigue, increased thirst, frequent urination, and damage to organs such as the kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
Insulin and fat storage
Insulin also plays a key role in regulating the storage of fat in the body. When we consume more calories than our body needs for energy, the excess calories are stored either as glycogen in the liver and muscles or as fat. Insulin signals the body to store fat by promoting the uptake of fatty acids and glucose into adipose tissue, where they are converted into triglycerides and stored as fat.
Insulin also inhibits fat breakdown in the body by suppressing lipolysis, the process by which stored fat is broken down into fatty acids and released into the bloodstream to be used for energy.
However, when insulin levels are chronically elevated, as is the case with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, excess fat storage can occur, leading to weight gain, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and other chronic health conditions.
Why is it important to maintain blood sugar levels?

Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Here are some reasons why:

1Diabetes prevention
Chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels and impaired glucose metabolism. Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help to prevent the development of type 2 diabetes and its complications.
2Obesity prevention
Insulin and obesity have a direct correlation that scientists have been studying for years. Problems with insulin sensitivity can make it almost impossible for an individual to lose weight. In individuals who are overweight or obese tend to have higher blood glucose levels and the other way around. Not only is obesity a significant risk factor for developing diabetes, but it can also contribute to other health issues, such as heart disease and stroke.
3Energy production
Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, including the brain. Maintaining normal blood sugar levels ensures that there is a steady supply of glucose available for energy production.
4Cardiovascular health
High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death worldwide. Maintaining normal blood sugar levels can help to protect against cardiovascular disease and improve overall cardiovascular health.
5Brain function
The brain relies on glucose as its primary source of fuel, and disruptions in blood sugar levels can affect cognitive function, mood, and behaviour. High blood sugar levels can cause fatigue, confusion, and difficulty concentrating, while low blood sugar levels can cause weakness, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness. According to research, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can impact cognitive function and brain structure, with an estimated 50% increased risk of dementia in type 2 diabetes.
 Source: National Library of Medicine
Source: National Library of Medicine 6Kidney function
High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys and impair their function, leading to chronic kidney disease and other complications. Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels can help to prevent kidney damage and preserve kidney function.
Problems with insulin functioning in the body

But sometimes, the body doesn’t always function as it should and insulin levels become imbalanced. This can have a detrimental effect on blood sugar levels and lead to a range of health problems such as:
Insulin resistance: This is a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to impaired glucose uptake and utilization. Insulin resistance is a key feature of type 2 diabetes and is often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and other lifestyle factors.
Hyperinsulinemia: This is a condition where the body produces too much insulin, leading to abnormally low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia). Hyperinsulinemia is a common feature of type 2 diabetes and can be caused by insulin resistance. Hypoglycaemia can be dangerous if not treated quickly.
Hypoinsulinemia: This is a condition where the body produces too little insulin, leading to abnormally high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). It can be caused by autoimmune destruction of the beta cells in the pancreas (type 1 diabetes) or other conditions that affect insulin secretion.
How to maintain healthy insulin levels

Maintaining healthy insulin levels is important for regulating metabolism, preventing chronic health conditions related to insulin resistance and obesity, and maintaining a healthy weight. Here are some tips for maintaining healthy insulin levels:
1. Follow a balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help to regulate insulin levels and promote a healthy metabolism. An unhealthy diet that is high in red meat, sweets, sugary drinks, and fried foods is proven to increase the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.

2. Manage carbohydrate intake: Consuming too many carbohydrates, especially refined carbohydrates like white bread and sweet pastries, can cause blood sugar and insulin levels to spike. Choosing complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, and combining them with lean proteins and healthy fats can help to regulate blood sugar and insulin levels.
3. Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help to promote healthy insulin levels.
4. Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help to improve insulin sensitivity and promote a healthy metabolism. The NHS recommends aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise a week.
5. Manage stress: Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can weaken insulin sensitivity and increase the risk of insulin resistance. Practising stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing, can help to promote healthy insulin levels.
6. Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can disrupt the body’s hormones and metabolism, leading to insulin resistance and other health problems. Sleep experts recommend aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to promote healthy insulin levels.
How to test insulin levels

Below are some of the common ways of testing insulin levels.
1. Blood glucose levels test: Measuring your blood glucose works as a proxy to find out if your insulin is functioning properly. This is the most common and simple way to evaluate your risks of insulin resistance and diabetes. If your fasting blood glucose levels are chronically high or too low, that might indicate some problems with insulin production or sensitivity.

There are several kinds of blood glucose tests, including laboratory testing, self-monitoring blood glucose (glucometer testing), and continuous glucose monitoring. You can explore the last method by reading our detailed article on this way of monitoring.
2. Fasting insulin test: This test is typically done after an overnight fast and measures the amount of insulin in the blood.
3. Glucose tolerance test: This test involves drinking a sugary solution and then measuring insulin and glucose levels at various intervals over several hours. It can help to diagnose insulin resistance and diabetes.
4. Haemoglobin A1c test: This test measures the average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months and can be used to diagnose diabetes and monitor blood sugar control.
If you have concerns about your insulin levels, talk to your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and treatment options. They can help to interpret the results of the test and provide guidance on maintaining healthy insulin levels.
Fun & curious facts
-
Insulin was discovered in 1921 by Sir Frederick Banting and Charles Best. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery.
-
Insulin is used to treat diabetes, but it has also been used by bodybuilders and athletes as a performance-enhancing drug, despite being banned by many sports organizations.
-
The first insulin injection was given to a 14-year-old boy named Leonard Thompson in 1922. Before insulin was discovered, people with diabetes had few treatment options and often did not live very long. Today, insulin is a life-saving medication for millions of people around the world.
Let’s sum up: The importance of insulin in regulating weight and metabolism

Insulin is a hormone that plays an essential role in regulating our weight and metabolism through its effects on blood sugar levels, fat storage and breakdown, and protein synthesis. When insulin levels are either too low or high, these regulatory mechanisms stop working properly which can lead to metabolic dysfunction, weight gain and a range of health problems, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance. Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is vital for good health and prevents complications associated with hyperglycaemia and hypoglycaemia.
By following our tips about how to maintain insulin levels, including getting regular exercise, eating healthily and managing stress, you can ensure your metabolism continues working as well as it can and maintain a healthy weight.
Hungry for knowledge? Here is more
In this video from Novo Nordisk, learn all about diabetes including how it affects the body, the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes and how insulin regulates blood sugar levels.