Thanks to our automatic nervous system we do not even notice how we make from 17,000 to 25,000 breaths per day. It seems that we start noticing how we breathe only when thinking about it. Due to taking the importance of breathing for granted, we do not pay attention to the way we breathe. Do you breathe lightly or take big inhales? Do you use your nose or mouth for breathing?
Answering these questions can provide us not only with explanations of why we are stressed or have a dry mouth in the morning. By being conscious about our breathing we can reduce the risks of premature death as well as positively contribute to our healthspan.
Here are the seven reasons why mouth breathing is killing your chances for long, disease-free life.
1Mouth breathing gives you less oxygen which may cause various diseases
Yes, if you breathe with a bigger airway you are not getting more oxygen. In fact, nasal breathing creates more resistance than mouth breathing, leading to 10-20% greater oxygen uptake. Plus, while breathing through the nose nitric oxide (NO) is emitted. It helps open the airways and increases oxygen uptake by the blood. The flow of blood to the lungs is also balanced by nitric oxide, which makes oxygen more easily transported. Furthermore, NO promotes better blood flow in the lungs by relaxing blood vessels. By breathing through our mouths, we miss out on these benefits. The concentration of NO that comes from the nose is 100 times higher than in the lower airways.
When you are not getting enough oxygen a myriad of health issues appears. Mouth breathing increases the risk of respiratory infections, sleep disorders, cognitive impairment, and even chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease.
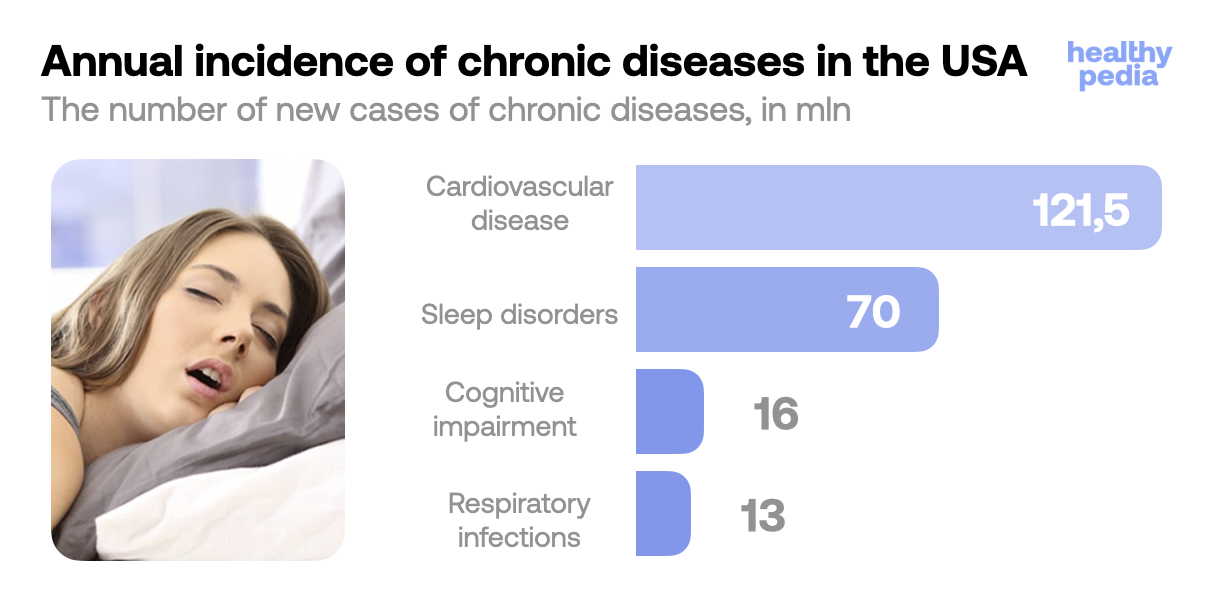 Source: World Health Organization
Source: World Health Organization Thus, inhaling and exhaling through your mouth makes you more susceptible to various diseases that cut down your lifespan. Have a look at the chart that shows how many people suffer from chronic conditions that may be contributed by mouth breathing. The numbers are fearsomely impressive. Of course, all of these conditions are caused by a complex of risk factors put together. However, while such risk factors as a family history of the disease or genetic predisposition cannot be eliminated, mouth breathing is definitely a thing that you can eradicate. Do not underestimate the power of your breath, as in some events mouth breathing can be the last straw in the bouquet of risk factors.
2Mouth breathing exacerbates stress
Stress is a disease risk factor that mustn’t be overlooked. The thing is that our mental health vastly influences our physical health. Stress triggers 75-90% of human diseases.
 Source: PubMed
Source: PubMed Mouth breathing increases stress because it can lead to an imbalance in the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body, resulting in the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s ‘fight-or-flight’ response. This can cause an increase in stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can have negative effects on the body, including increased heart rate, blood pressure, and anxiety.
The findings of a study showed that young rats, that experienced a brief blockage of the nasal passage, had a 1,000% increase in stress hormones. Even though, a similar study on humans hasn’t been conducted yet, stress exacerbating the effect of mouth breathing can be proven by the fact that 75% of people who suffer from anxiety have disordered breathing.
Eradicating the stress stimuli that the outer world brings can be hard and sometimes impossible, but beginning nose breathing and promoting relaxation and expelling stress hormones is more than possible.
3Mouth breathing impairs sleep and causes sleep apnea
Sleep is a fundamental part of our life. The world’s longest record of not sleeping is 11 days (264 hours). However, being up for 24-48 hours causes severe detrimental results. Sleep apnoea is when your breathing stops and starts while you sleep. People who breathe through their mouths are at a higher risk of developing sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a risk factor for myriad diseases.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is closely associated with hypertension. Around 50% of people who have OSA suffer from high blood pressure, and between 30% and 40% of hypertensive patients have OSA.
A fatal loss of heart function was recorded in 46% of OSA patients, compared with 21% of people without OSA.
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance increases if you suffer from sleep apnea. OSA may also trigger metabolic syndrome that causes high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, and high blood sugar and is linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
Research has shown that obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) can contribute to the development of depression. Up to 67% of people with OSA also experience insomnia, and depression scores are higher in individuals presenting with both insomnia and OSA.
 Source: PubMed
Source: PubMed What is more, besides killing our health, sleep apnea also increases the risk of getting into an accident. A study conducted in 2020 found that over 26% of drivers hospitalized after car accidents were at a high risk of obstructive sleep apnea. Pilots falling asleep while flying has also been reported, with over half of pilots admitting to falling asleep while in charge of a plane and 29% waking up to find their co-pilot asleep as well.
It is important to consult your doctor if you notice any symptoms of sleep apnea in order to save your own life and life of those around you.
4Mouth breathing makes asthma symptoms worse
Asthma is a condition where the small airways in the lungs get swollen and narrow, making it hard to breathe. This can cause symptoms like coughing, wheezing, feeling short of breath, and tightness in the chest. Annually, it affects 262 million people and caused 455 000 deaths.
Mouth breathing and asthma usually go side by side. It has also been shown that mouth breathing is associated with decreased lung function in people with asthma, as well as worsening asthma symptoms.
Mouth breathing can cause lower respiratory tract infections due to the inhalation of dry, cold, or polluted air, which can irritate the bronchial tubes and cause inflammation. Lower respiratory tract infections have been linked to asthma development and are known to exacerbate asthma symptoms. An older asthma patient may experience a different, more severe variant of asthma associated with deteriorating immune function.
In a study of 10000 Japanese citizens, mouth breathing was reported by 17% of the population and was linked to asthma morbidity. The risk for asthma morbidity was 85% in subjects with mouth breathing.
 Source: PubMed
Source: PubMed 5Mouth breathing elevates risks of cardiovascular diseases
For our cardiovascular system to function properly we need oxygen. And mouth breathing does not enrich the body with as much O₂ as nasal breathing does. Insufficient amount of oxygen causes impairment of cardiovascular function. It may lead to confusion, restlessness, difficulty breathing, rapid heart rate, and bluish skin.
Studies have indicated that sleep disorder breathing (mouth breathing is one of its characteristics) is linked with a high risk of serious disease including sudden death, stroke, coronary artery disease, and heart failure. Habitual snoring, a result of night mouth breathing, was associated with a 25% higher stroke risk.
 Source: PubMed
Source: PubMed According to a study involving over 10,000 people over a five-year period, those with hypoxemia (significant drops in nighttime oxygen levels) were almost twice as likely to experience sudden cardiac death.
Cardiovascular diseases like stroke and coronary artery disease are the top killers of humanity claiming 6.5 million and 8.9 million lives annually. In contrast to other diseases death from these two maladies usually comes suddenly. That is why it is of utmost importance to ensure nasal breathing for the heart’s sake.
6Mouth breathing increases the risks of Alzheimer’s disease
Mouth breathing also deteriorates brain function. A recent Japanese study found that rats forced to breathe through their mouths since their nostrils were blocked developed fewer brain cells and took twice as long to navigate a maze as rats who breathed through their noses.
Interesting Fact from Healthypedia
The ancient Chinese called mouth breathing ‘Ni Ch’i’ which means an adverse breath. They believed that the breath inhaled through the mouth is extremely harmful.
Our brain can endure a maximum of 4 minutes without O₂ then the brain cells start dying. By impairing brain function, much breathing may contribute to Alzheimer’s and dementia development.
The study enrolled 127 participants, and those with sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) showed greater brain changes associated with Alzheimer’s disease, including greater amyloid burden, grey matter volume, perfusion, and metabolism. The study suggests that screening and treating SDB, even in asymptomatic older populations, may reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
A sharp brain is a guarantee of healthy ageing, so it is important to get rid of all the stimuli that can trigger brain dysfunction.
7Mouth breathing depraves kidney function
Kidney is an organ that makes our body flush all the wastes and toxins out. When using the mouse for breathing, our lungs are booming an external organ meaning nothing protects the body from air pollutants coming inside. The act of mouth breathing reduces the release of vasopressin, a hormone that eventually affects kidney function and fluid balance in the body.
Obstructive sleep apnea has been proven to be a risk factor for diabetic kidney disease (DKD). A study was conducted on 214 DKD patients to compare their urine tests based on the severity of OSA. The study found that patients with severe OSA had higher albumin content in urine (meaning that their kidneys were ill because a damaged kidney lets some albumin pass into the urine) compared to those with moderate or mild OSA. The study concludes that severely disrupted sleep breathing is linked to a decline in kidney function.
Thus, it is essential to breathe through the nose in order to maintain kidney health. The importance of this organ cannot be overlooked as kidneys ensure the health of the whole body by maintaining the body’s fluid balance, regulating blood pressure, and producing hormones that stimulate red blood cell production.

Let’s summarise

Take a moment to reflect on your breathing habits. Are you a mouth breather or a nasal breather? As we’ve learned, mouth breathing has a quality of exacerbating risks of respiratory infections, sleep disorders, cardiovascular diseases, asthma, and even Alzheimer’s. By being conscious of your breathing and making the switch to nasal breathing, you can reduce your risk of disease and prolong your life. Remember, a healthy breath equals a healthy life. A healthy breath equals a healthy life.
Not enough? Here are some more from our colleagues
We highly recommend the book Breath: The New Science of a Lost Art by James Nestor for anyone interested in the fascinating science of breathing and its impact on our health, fitness, and overall well-being. Through personal anecdotes, historical research, and cutting-edge science, Nestor takes readers on a journey of discovery about the power of breathing and how we can optimize our breath to live healthier and happier lives. This book is a must-read for anyone seeking to better understand the importance of proper breathing techniques and the many benefits they offer.