Heat exposure therapy might sound like a torturous punishment, but it’s actually more like a rejuvenating spa treatment. Imagine being wrapped up in a toasty sauna, or sinking into a hot bath after a long day – that’s heat exposure therapy. And while you’re relaxing in the heat, your body is hard at work, releasing endorphins and hormones to boost your energy and help you say goodbye to stress.
But how exactly does heat exposure affect your hormones? The parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems play a significant role, and when the body is exposed to heat, adrenaline, cortisol, endorphins, and oxytocin are some of the hormones that can be impacted. In this article, we’re turning up the heat and delving into the effects of heat exposure therapy on hormone levels in the body and how they make you feel.
What is heat exposure therapy?

Heat exposure therapy, also known as hyperthermia therapy, is a treatment that involves exposing the body to high temperatures to stimulate healing and improve overall health. This therapy has been used for centuries in traditional medicine, and it is now gaining popularity in modern medicine as a complementary treatment for various conditions and to support general health and well-being.
There are several ways that heat exposure therapy can be administered, including:
-
Sauna therapy: This involves sitting in a room with temperatures between 160°F to 200°F (71°C to 93°C) for a period of time. The body’s core temperature increases, which can lead to sweating and an increase in heart rate. Sauna therapy has been shown to improve cardiovascular health, reduce stress and anxiety, and help with pain management.
-
Infrared therapy: This involves using infrared light to heat the body directly. Infrared therapy is often used to treat conditions such as chronic pain, arthritis, and inflammation.
-
Hot water therapy: This involves soaking in hot water, such as a hot tub or bath. Hot water therapy has been shown to improve circulation, reduce stress, and help with muscle relaxation.
-
Whole-body hyperthermia: This involves using special equipment to increase the body’s core temperature to a fever-like state. Whole-body hyperthermia is used as a complementary treatment for cancer and has been shown to improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
The role of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems

Now, we can’t talk about heat exposure therapy without discussing the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. These two systems work together to maintain our internal balance, also known as homeostasis. The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for our rest and digest state. It slows our heart rate, increases digestive activity, and decreases our blood pressure. The sympathetic nervous system, on the other hand, is responsible for our fight-or-flight response. It increases our heart rate, dilates our pupils, and releases adrenaline to prepare us for action.
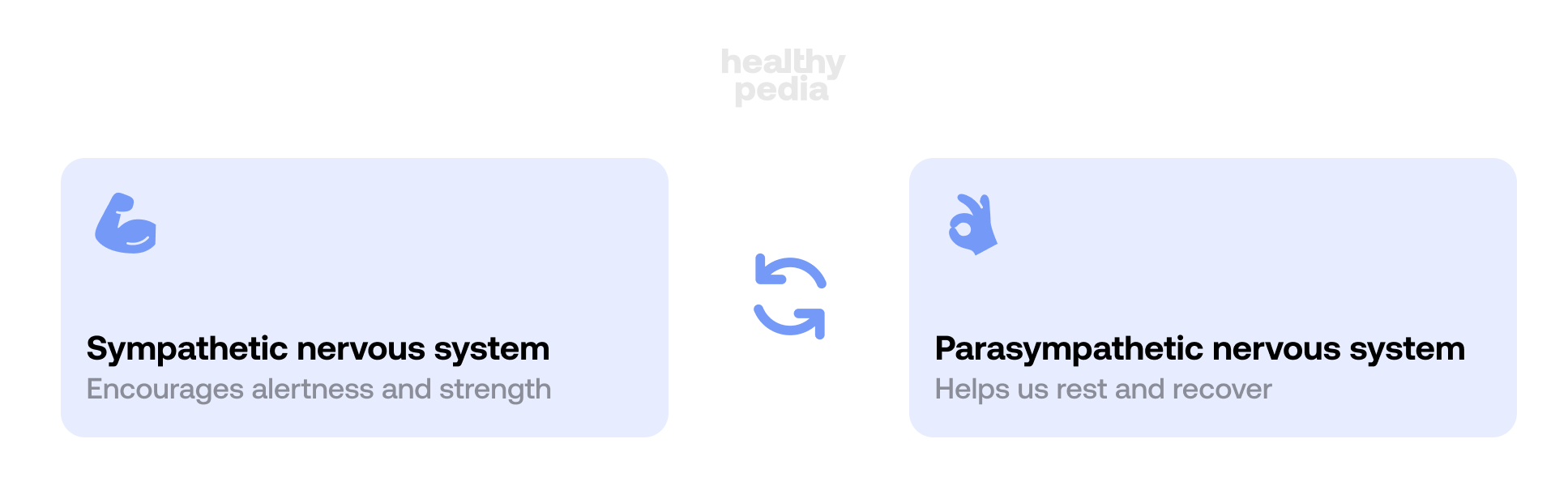
So, how do these two systems come into play during heat exposure? Well, when our bodies are exposed to heat, our parasympathetic nervous system kicks in, and we begin to sweat to cool down. This helps to lower our internal temperature and keeps us from overheating. However, if we are exposed to heat for an extended period, our sympathetic nervous system can also kick in. This increases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration rate, which help the body cope with the stress of heat exposure.
How heat exposure affects your hormones

Heat exposure therapy can affect hormones in several ways, as the body responds to increased temperatures by activating various physiological mechanisms. The following are some of the ways that heat exposure therapy can impact hormone levels.

1Gives adrenaline energy boost
Adrenaline prepares the body for a fight-or-flight response by activating the sympathetic nervous system. This increases blood flow to the muscles and other major organs, dilates air passages to provide muscles with more oxygen, and increases the availability of glucose to provide energy.
It is released in response to stressful situations, such as heat exposure therapy, as its effects help the body cool down and cope with extreme temperatures. Adrenaline can make you feel energized, alert, and ready for action, helping you tackle your day with power and vigour!
Adrenaline can also have remarkable effects on people with type 1 diabetes. People with this diagnosis lack the ability to produce insulin, and eventually lose their capacity to secrete glucagon. This puts them in great need of adrenaline for maintaining a normal blood sugar level – without it, extreme hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) unawareness can have dire consequences. According to research, adrenaline can help prevent hypoglycaemia because it temporarily increases the amount of glucose in the blood.
2Makes you lose cortisol and stress
Cortisol is also known as the stress hormone because it is released in response to, you guessed it, stress. It boosts blood sugar levels, conserves energy for essential processes, and prepares muscles for action. But, sustained high levels of cortisol can lead to feelings of anxiety and tension and can have other negative effects on our health.
When the body is exposed to heat, it can lead to muscle relaxation and increased blood flow, which can help reduce tension and stress. This physical relaxation can also help reduce cortisol levels in the body.
One study, which looked at the effects of thermal stress in young men, found that after 72 minutes of sauna treatment, cortisol levels decreased from 13.61 to 9.67 µg/ml.
 Source: National Library of Medicine
Source: National Library of Medicine 3Triggers the release of feel-good endorphins
Endorphins are the body’s natural painkillers and mood enhancers that are released in response to stress, pain, or exercise. When the body is exposed to heat, it can trigger the release of endorphins, which can help reduce pain, improve mood, and promote relaxation.
Research has shown that heat exposure therapy, such as using a sauna or taking a hot bath, can lead to an increase in endorphin levels in the body. This gives you a natural high, promoting feelings of euphoria and relaxation.
Additionally, the release of endorphins can have long-term effects on the body. Regular heat exposure therapy has been shown to help reduce chronic pain, improve mood, and promote overall well-being.
4Makes you feel the love with oxytocin
Heat exposure therapy can make you feel all warm and fuzzy inside, and that’s not just because of the temperature! It turns out that heat exposure therapy can also increase the release of oxytocin, the “love hormone,” in the body.
Oxytocin is a hormone that is released in response to social bonding, touch, and intimacy, and it can lead to feelings of love, trust, and connection. When you’re basking in the heat of a sauna or soaking in a hot bath, your body may release more oxytocin, which can make you feel more relaxed, happy, and connected to those around you.
One study found that increasing levels of oxytocin in the body improved self-perception in social situations and enhanced personality traits like warmth, trust, and altruism.
5Boosts the levels of growth hormone
As we age, growth hormone secretion decreases and can lead to an increase in obesity-related fragility. Heat exposure through sauna use has been shown to produce a transient release of this valuable hormone – with duration, temperature, and frequency playing key roles in the degree of elevation. For example, two 20-minute sessions at 80 °C (176 °F) yielded twice as much growth hormone than baseline whereas 15 minutes at 100 °C (212 °F) saw levels five times higher.
Extended sauna sessions may have an immediate and profound effect on growth hormone levels; a study of 17 male and female participants found that after seven consecutive days in 80°C (176°F) dry heat, their concentrations had increased by up to 16 times.
 Source: ScienceDirect
Source: ScienceDirect Additionally, results showed that combining exercise and sauna usage can further stimulate this release of growth hormone, creating even greater benefits to users.
6Releases relaxing prolactin
Prolactin is a hormone that is typically associated with breastfeeding, but it also plays a role in relaxation and stress reduction. When you expose your body to heat, it can trigger the release of prolactin, which can help reduce stress and promote a sense of calm.
7Gets you buff with testosterone
Heat exposure therapy can do more than just relax your muscles and give you a glowing complexion, it can also increase testosterone levels. This can lead to improved muscle mass, strength, and energy levels. So, for those looking to channel their inner Hercules, a little heat exposure therapy might just do the trick!
One study that looked at the effects of administering testosterone to male participants found that increasing levels of testosterone in the body could increase muscle protein synthesis by 27%. Muscle protein synthesis is the process by which new muscle is built.
Fun facts about heat exposure therapy
-
Saunas can be used as a form of socializing. In Finland, saunas are seen as a gathering place where friends and family can come together to relax and socialize. It’s not uncommon for business meetings or political discussions to take place in a sauna setting.
-
In the early days of space exploration, astronauts used saunas to simulate the effects of exercise on their bodies in zero-gravity conditions. The heat exposure helped to increase blood flow and maintain cardiovascular health while in space.
Let’s sum up

Regular heat exposure and use of sauna promote positive hormonal changes in the body. It temporarily increases levels of adrenaline, endorphins, oxytocin, testosterone, growth hormone, and prolactin, and decreases the levels of cortisol. All these changes make you feel relaxed yet energized and powerful. If your routine doesn’t already include the use of a sauna or a heated room then it could be worth considering integrating such a practice into your lifestyle in order to reap these health benefits and further improve your physical and mental wellbeing.
Hungry for knowledge? Here is more
In this video, neuroscientist Andrew Huberman discusses how heat exposure impacts body temperature, metabolism, heart health, hormone production, exercise recovery, cognition, mood, and longevity.