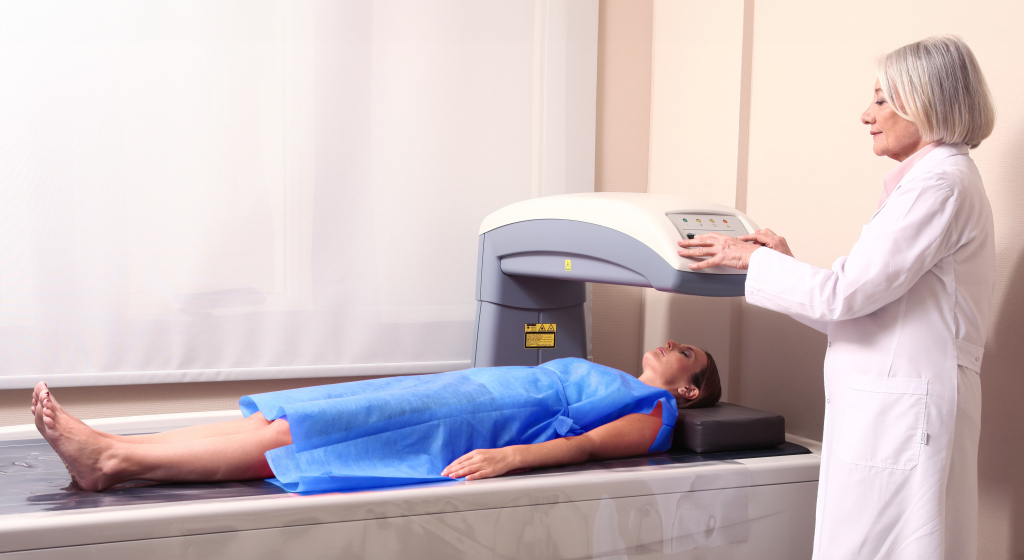
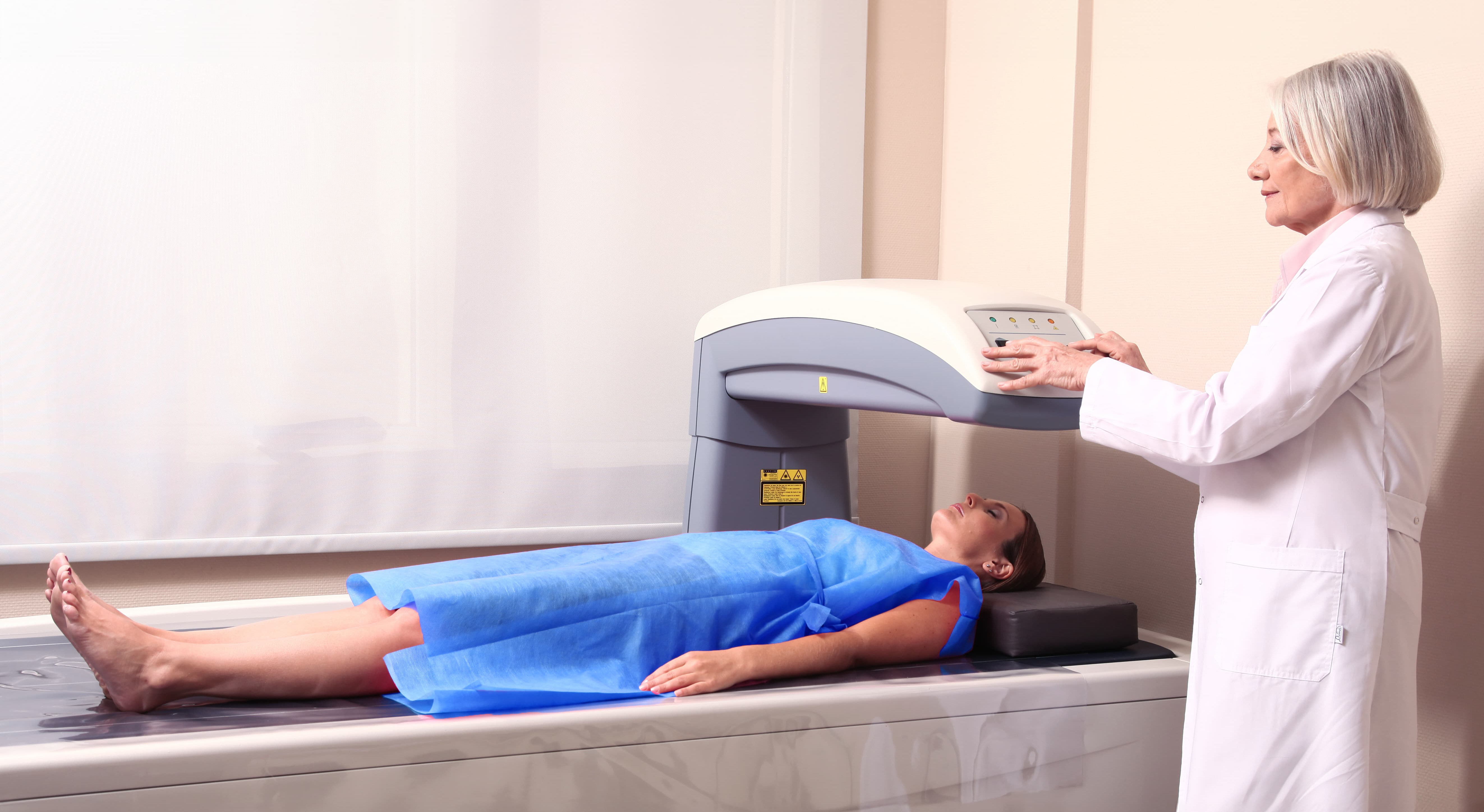
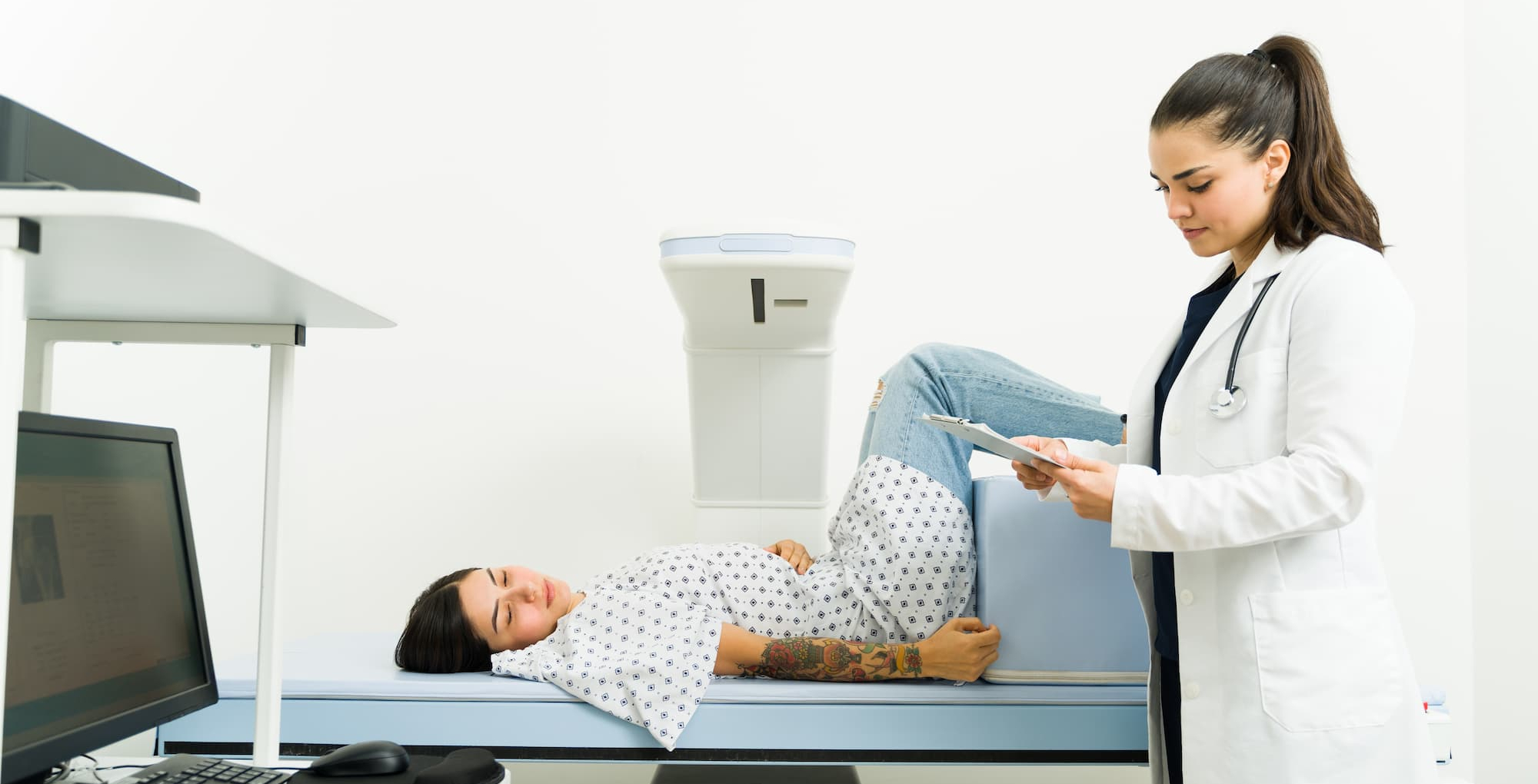
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) is a medical imaging technique used to measure bone density and body composition. It provides detailed images of bone and soft tissue, allowing for the assessment of bone health, fat, and lean muscle mass. DEXA is commonly used in sports medicine to monitor athletes’ body composition, track changes over time, and optimize performance.
How much radiation is there during the scan?

DEXA scans involve a minimal amount of radiation. The effective dose from a single whole-body scan ranges between 2 and 10 microsieverts (µSv). To put this in perspective, the annual natural background radiation in the UK is around 1,000 µSv.
A DEXA scan’s radiation is significantly lower than that from a chest X-ray (approximately 14 µSv) and vastly lower than a CT scan of the trunk, which can range from 6,000 to 10,000 µSv. This minimal radiation level makes DEXA a safe option for repeated use, particularly when compared to other radiographic procedures.
Limits on safe levels of radiation in the UK

In the UK, the safety of radiation exposure is regulated by The Ionising Radiation (Medical Exposure) Regulations 2017. These regulations ensure that any medical exposure to radiation is justified and optimized to keep the dose as low as reasonably achievable. For the general population, an incremental increase in radiation dose should be evaluated against the natural background radiation.
Given the low radiation dose from a DEXA scan, the incremental risk is minimal. It is estimated that a single DEXA scan increases the lifetime risk of cancer incidence by less than 1 in 1 million, based on linear no-threshold (LNT) extrapolation from high-dose levels.
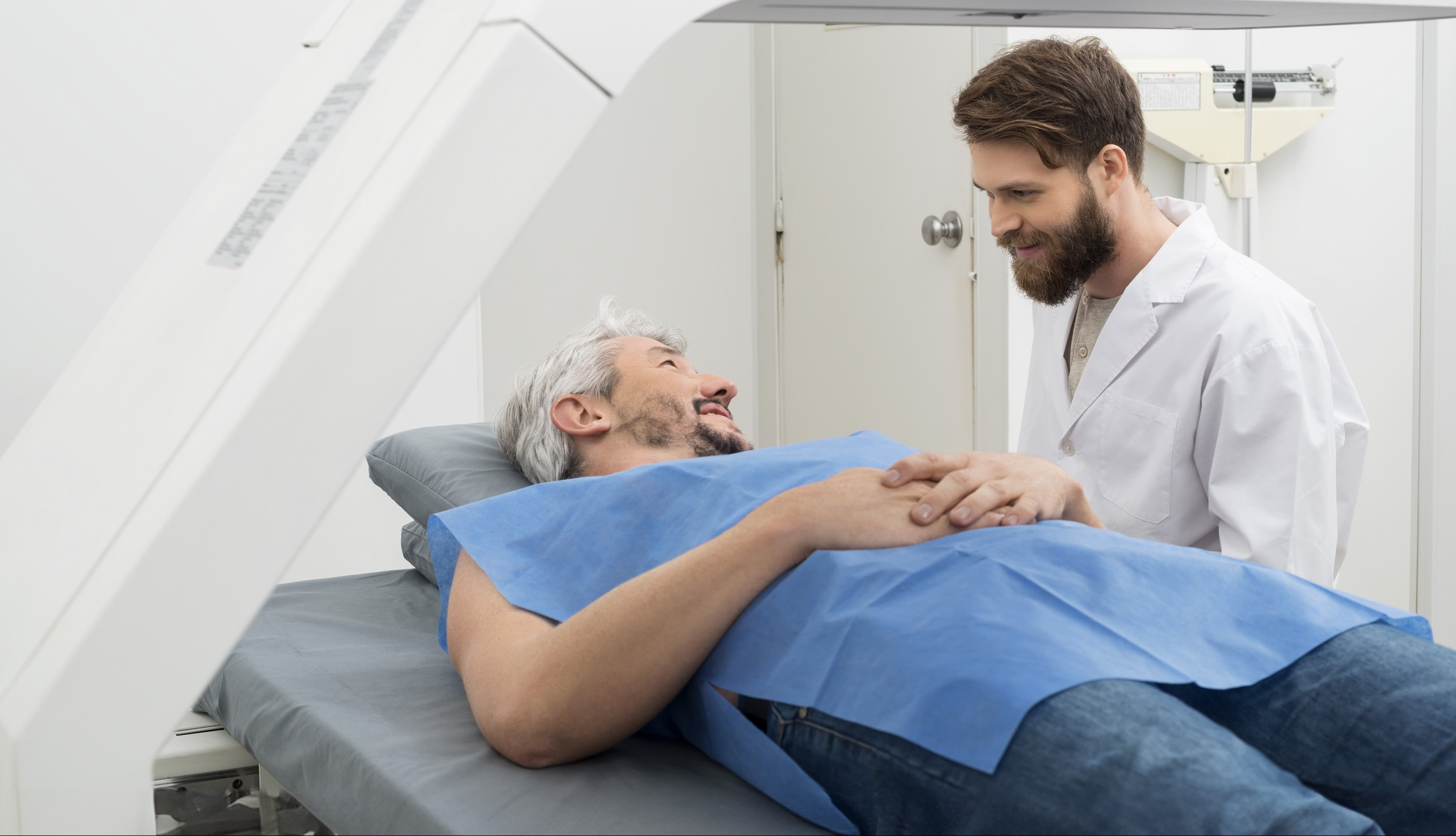
How often can you do the scan?

The frequency of DEXA scans depends on individual health needs and medical advice. For athletes or individuals monitoring body composition as part of a training program, periodic scans may be recommended. While the radiation dose from a single scan is very low, the cumulative dose from multiple scans over several years should be considered.
The minimal dose per scan allows for multiple assessments annually, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine a safe and appropriate schedule based on individual circumstances.
Let’s sum up!

DEXA scans provide valuable information about bone density and body composition with a very low level of radiation. The effective dose from a single scan is minimal, making it safe for repeated use under medical guidance. In the UK, regulations ensure that any exposure to radiation is justified and kept as low as possible. Athletes and individuals undergoing training programs can benefit from periodic DEXA scans, but it’s important to balance the benefits with the cumulative radiation dose over time.